Standalone Designer's Query Designer
Standalone Report Designer provides both a graphical and a text-based query designer to help you create queries to retrieve data from a relational database for a SqlDataSource component. The Query Designer supports any ADO.NET/ODB/OLEDB data provider with a working implementation of GetSchema with COLUMN collection support. Automatic relations functionally require relational databases supported by Telerik Data Access:
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Microsoft SQL Server Compact Edition
- Microsoft SQL Azure
- Oracle
- MySql
- Advantage Database Server
- SQL Anywhere
- Firebird
- VistaDB
- SQLite
- PostgreSQL
Please note that Telerik Data Access is a discontinued product and its supported databases list will not be appended. The versions of the supported database drivers will not be updated as well.
The following figure shows the graphical query designer.
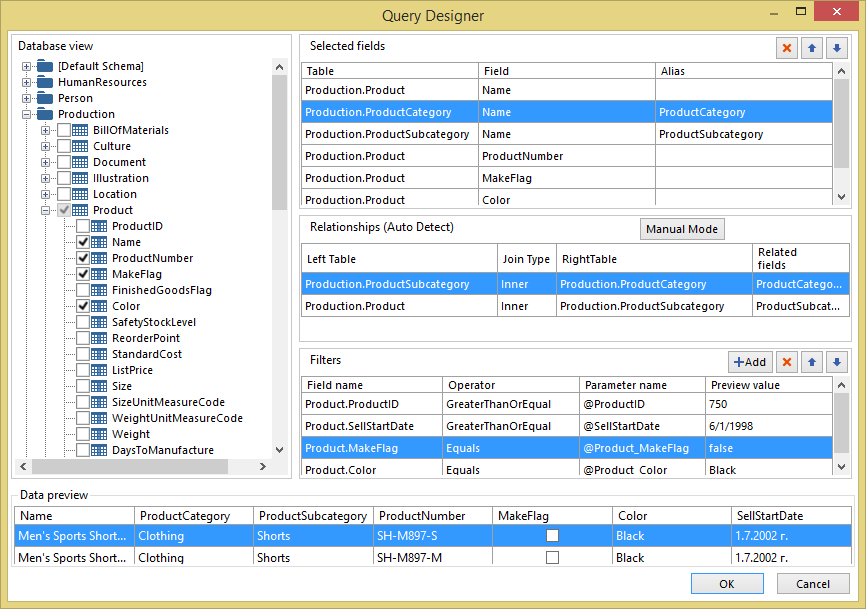
Use the graphical query designer to explore the database tables and views, interactively build SQL SELECT statements, and view the result. The select statement specifies the database tables, views, and columns from which to retrieve data for a SqlDataSource Component. If you choose multiple related tables, the query designer describes the relationship between sets of two tables.
Schema Restrictions
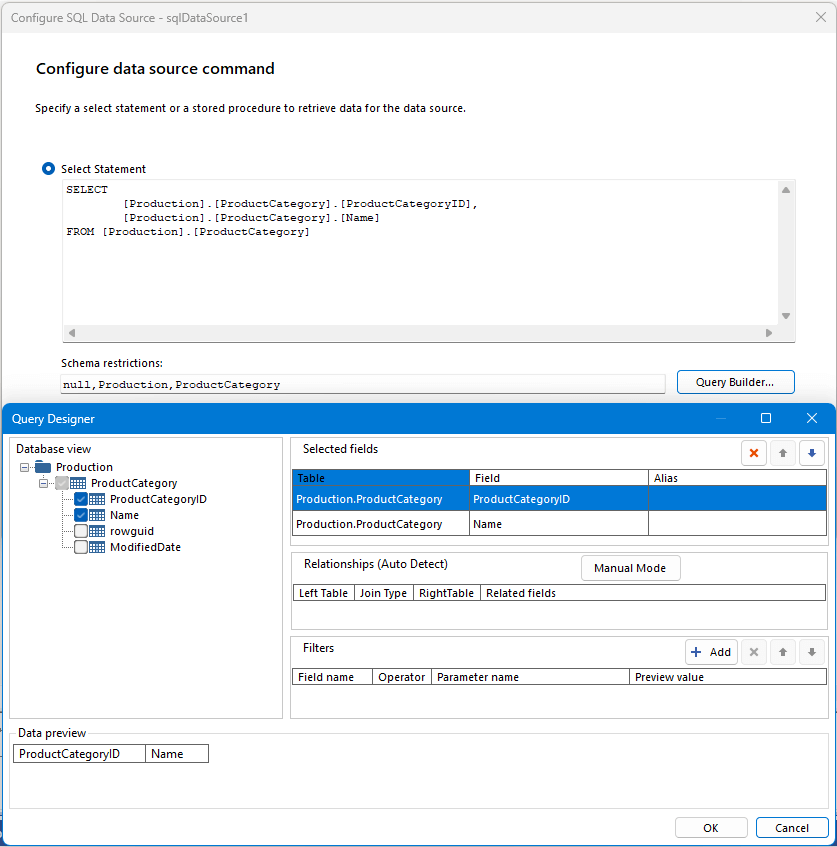
As of 2025 Q1, the Query Builder of the Standalone Report Designer accepts a new property called SchemaRestrictions. The value of this property is a comma-separated list of schema restrictions that will be used by the chosen data provider to query a subset of data from the database schema. This allows report creators to load only the necessary schema information and benefit from faster load times.
Behind the scenes, the Reporting engine calls the ADO.NET GetSchema method on the columns collection and passes the schema restrictions specified by the user. The exact number and order of schema restriction arguments can vary depending on the selected data provider. For example, provided we have a connection to the Microsoft SQL Server AdventureWorks sample database, we can pass the following string to the schema restrictions field to instruct the Query Builder to load the schema of the ProductCategory table only.
null,Production,ProductCategory
Schema restrictions are case-sensitive and empty arguments are respected. If you need to provide a null value for a specific argument, you can use the
nullkeyword as demonstrated in the example above. The schema restrictions work only with .NET 8+.
Query Designer Panes
The following sections describe the function of each pane.
- Database View Displays a hierarchical view of tables and views that are organized by database schema.
- Selected Fields Displays the list of database field names from the selected items in the Database View pane.
- Relationships Displays a list of relationships that are inferred from the selected tables or views or the relationships that you created manually.
- Filters Displays a list of filter criteria for tables or views.
- Data Preview Displays sample data for the automatically generated query.
Database View Pane
The Database View pane displays the metadata for database objects that you have permission to view. The permission is determined by the data source connection and credentials. The hierarchical view displays database objects organized by database schema. Expand the node for each schema to view tables and views. Expand a table or view to display the columns.
Selected Fields Pane
The Selected Fields pane displays the selected columns to include in the query. The fields displayed in this pane become the field collection for the report data item. These fields represent the data you can display in tables, graphs, and other report items when you view a report.
The following options are available:
- Delete Deletes the selected field from the fields collection.
- Move Up or Move Down Moves fields up or down the fields list. The fields are added to the query in the order they appear in the Selected Fields list.
The following columns are displayed:
- Table Displays the field table name.
- Field Displays the field name.
- Alias The alias to use for the field. The alias will be automatically generated if the last added field name is already in use. Additionally, field aliases can be changed or added manually.
Relationships Pane
The Relationships pane displays the join relationships. The relationships can be detected automatically from the foreign key relationships that are retrieved from the database metadata or you can create them manually.
The following options are available:
- Manual Mode/Auto Detect Toggles the auto-detect feature that automatically creates relationships between tables. If auto-detect is turned on, the query designer creates relationships from foreign keys in tables; otherwise, you must create the relationships manually. When you select tables in the Database View pane, auto-detect automatically attempts to create relationships. If you turn on auto-detect after you have manually created joins, those joins will be discarded.
- Add Relationship Adds a relationship to the Relationship list. If auto-detect is turned on, the tables from which columns are used in the query are automatically added to the Relationship list. When auto-detect identifies that two tables are related, one table is added to the Left Table column, the other to the Right Table column, and an inner join is created between them. Each relationship generates a JOIN clause in the query. If the tables are not related, all of them are listed in the Left Table column and the Join Type column indicates the tables are not related to other tables. When auto-detect is turned on, you cannot manually add relationships between tables auto-detected as unrelated. In manual mode, you can add and change relationships between tables. Click the Related Fields cell to specify the fields to use to join the two tables. When using multiple relationships in a query, one of the tables in each relationship, except the first one, must be referenced in a proceeding relationship.
- Delete Deletes the selected relationship from the relationships collection.
- Move Up or Move Down Moves relationships up or down the filter list. The relationships are added to the query in the order they appear in the Relationships list. Still, the SQL query builder may reorder the relationships to create a correct SQL statement.
The following columns are available:
- Left Table Displays the name of the first table that is part of a join relationship.
- Join Type Displays the type of SQL JOIN statement that is used in the automatically generated query. By default, if a foreign key constraint is detected, INNER JOIN is used. Other join types can be LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN. If none of these join types apply, the Join Type column displays Unrelated. No CROSS JOIN joins are created for unrelated tables; instead, you must manually create relationships by joining columns in the left and right tables.
- Right Table Displays the name of the second table that is part of a join relationship.
- Join Fields Lists the pairs of joined fields. If a relationship has multiple join conditions the pairs of joined fields are separated by commas (,).
- Related Fields Displays the relationships between the tables. Clicking a Related Fields cell while in manual mode opens a dialog box in which to add and modify relationships between tables. You choose the fields in the right and left tables to join. You can join multiple fields from the left and the right table to specify multiple join conditions in a relationship. The two fields that join the left and right tables do not need to have the same name. The joined fields must have compatible data types.
Filters Pane
The Filters pane displays the criteria that are used to limit the number of data rows that are retrieved at run time. Criteria specified in this pane are used to generate an SQL WHERE clause.
The following columns are displayed:
- Field Name Displays the name of the field to apply the criteria.
- Operator The operator to use in the filter expression.
- Parameter name The parameter name to add to the query.
- Preview value The value to use for the Data Preview pane.
The following options are available:
- Add Add a new filter to the filters collection.
- Delete Deletes the selected filter from the filters collection.
- Move Up or Move Down Moves fields up or down the filter list. The filters are added to the query in the order they appear in the Filters list.
Data Preview Pane
The Data Preview pane displays the results for the automatically generated query that is specified by selections in the other panes. The columns in the result set are the fields that you specify in the Selected Fields pane.
The data is not saved in the report definition. The actual data in the report is retrieved when the report is processed.
Sort order in the result set is determined by the order the data is retrieved from the database. The sort order can be changed after the data is retrieved for the report data item by adding sorting expressions with the Edit Sorting Dialog.
You can group the data and use aggregates after the data is retrieved using the report data item grouping abilities and Expressions.
Query Designer State
Clicking OK the SqlDataSource Wizard Select Statement will be replaced with the currently generated SQL query. The OK button is only enabled if the query is valid.
The Query Designer keeps the current setup state. However, if you modify the SQL query outside it and then use the Query Designer, it will override the SQL query manually made modification.