Trust Fiddler's Certificate Authority
Proper installation and trust of the Fiddler Everywhere Certificate Authority (CA) is essential for capturing and decrypting HTTPS traffic at the system level. This article explains the recommended and manual approaches for installing the Fiddler CA on Windows, macOS, and Linux, and provides troubleshooting tips and best practices.
CA installation is not required if you use independent browser capturing or terminal capturing modes.
Recommended: Automated CA Installation
The easiest and most reliable way to install and trust the Fiddler CA certificate is through the in-app system capturing wizards:
- Open the Home pane in Fiddler Everywhere.
- Start the System Proxy tutorial and follow the prompts. You will be guided to install and trust the Fiddler CA certificate in your OS certificate manager.
Once installed, the CA remains valid until explicitly uninstalled. The CA appears as Fiddler Root Certificate Authority in your OS certificate manager.
Manual CA Installation (Advanced)
Use the manual approach if the automated wizard fails or you need more control over the installation steps. Follow the instructions for your operating system:
Windows
- Go to Settings > HTTPS in Fiddler Everywhere.
- Click Trust Fiddler CA in the User Store. Confirm and accept the certificate in the popup.
To install the CA in the Windows machine store (for all users), run Fiddler as Administrator and use Trust Fiddler CA in the Machine Store.
- Go to Settings > HTTPS once more and enable Capture HTTPS traffic
- Click Save.
- On the main screen, toggle System Proxy ON to start capturing system HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
macOS
- Go to Settings > HTTPS in Fiddler Everywhere.
- Click Trust Fiddler CA in the User Store.
To install the Fiddler CA certificate in the system keychain, you must use the export option and then proceed with manually installing it on macOS. The Fiddler Everywhere application automatically recognizes the installed CA from the login and system keychains.
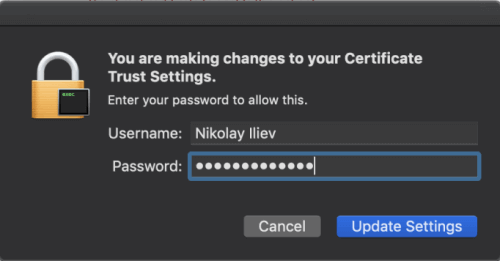
- Enter your macOS admin credentials when prompted.
- Go to Settings > HTTPS once more and enable Capture HTTPS traffic
- Click Save.
- On the main screen, enable Live Traffic to start capturing system HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
Linux
Go to Settings > HTTPS > Export in Fiddler Everywhere. Export the CA certificate in DER/Binary format. The file will be saved as Fiddler_Root_Certificate_Authority.crt on your Desktop.
-
Import and trust the exported certificate:
Some Linux distributions use localized Desktop folder names. If needed, create a
~/Desktopdirectory before exporting.sudo mkdir -p /usr/share/ca-certificates/extra sudo cp ~/Desktop/Fiddler_Root_Certificate_Authority.crt /usr/share/ca-certificates/extra sudo dpkg-reconfigure ca-certificatesIf your distribution does not use
dpkg, refer to your OS documentation or see our Fedora, CentOS, RedHat and XFCE guides. In the prompt, select Yes to install new certificates, then select the Fiddler certificate and confirm.
Enable Capture HTTPS traffic and click Save.
On the main screen, toggle System Proxy ON to capture system HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
Exporting the Fiddler CA (for Manual or Third-Party Use)
If automatic installation fails (due to security restrictions, permissions, or corporate policy), you can export the Fiddler CA and install it manually:
- Go to Settings > HTTPS.
- Choose the desired format (DER/Binary, PEM/ASCII, or PKCS 12) and click Export.
- Add the exported certificate to your certificate manager (see Linux, macOS, or your application documentation).
- Enable Capture HTTPS traffic and click Save.
- Enable System Proxy to start capturing system traffic.
Installing in Third-Party Certificate Stores
Fiddler CA can be exported in multiple formats for use in other applications:
Best Practices & Troubleshooting
- Always install the CA certificate only from the official Fiddler Everywhere application.
- Use the User Store for personal development; use the Machine Store only if multiple users need HTTPS capture.
- Remove the CA certificate when you no longer need HTTPS capturing for security.
- If HTTPS capture does not work, verify the CA is trusted and "Capture HTTPS traffic" is enabled.
- For certificate errors on specific sites, add the domain to the ignore list (for development only).
- On Linux, always follow the manual export and trust instructions for your distribution.
- Use independent browser capturing if you lack admin rights or only need browser traffic.