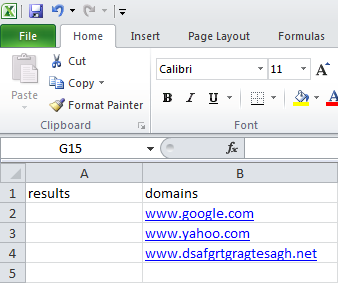
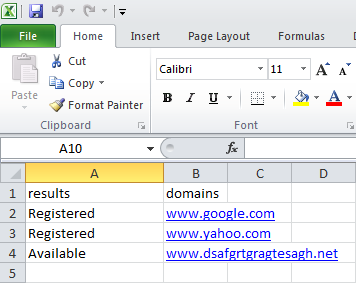
Here's a sample test that automates this case:
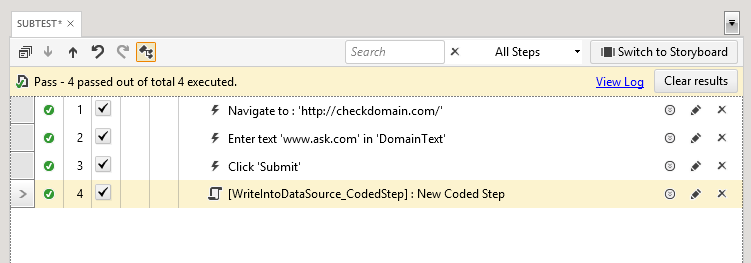
Note Ensure you Add an Assembly Reference to Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel. You can download a version of that file on Microsoft's website that matches your version of MS Office.
Here's the code from that sample:
string dataSourcePath = this.ExecutionContext.DeploymentDirectory + @"\Data\domainResults.xlsx";
string myPath = "C:\\domainResults.xlsx";
if (!System.IO.File.Exists(myPath))
{
System.IO.File.Copy(dataSourcePath, myPath);
}
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excelApp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook workbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(myPath);
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
ActiveBrowser.RefreshDomTree();
if (ActiveBrowser.ContainsText("already been registered"))
{
excelApp.Cells[Data.IterationIndex + 2 , 1] = "Registered";
}
if (ActiveBrowser.ContainsText("is still available"))
{
excelApp.Cells[Data.IterationIndex + 2 , 1] = "Available";
}
excelApp.Visible = true;
excelApp.ActiveWorkbook.Save();
workbook.Close(false, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
excelApp.Workbooks.Close();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(workbook);
excelApp.Quit();
GC.Collect();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelApp);
Dim dataSourcePath As String = Me.ExecutionContext.DeploymentDirectory + "\Data\domainResults.xlsx"
Dim myPath As String = "C:\domainResults.xlsx"
If Not System.IO.File.Exists(myPath) Then
System.IO.File.Copy(dataSourcePath, myPath)
End If
Dim excelApp As New Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application()
Dim workbook As Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(myPath)
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000)
ActiveBrowser.RefreshDomTree()
If ActiveBrowser.ContainsText("already been registered") Then
excelApp.Cells(Data.IterationIndex + 2, 1) = "Registered"
End If
If ActiveBrowser.ContainsText("is still available") Then
excelApp.Cells(Data.IterationIndex + 2, 1) = "Available"
End If
excelApp.Visible = True
excelApp.ActiveWorkbook.Save()
workbook.Close(False, Type.Missing, Type.Missing)
excelApp.Workbooks.Close()
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(workbook)
excelApp.Quit()
GC.Collect()
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelApp)
1. Make sure that during the installation of Microsoft Office .NET Programmability Support was selected.
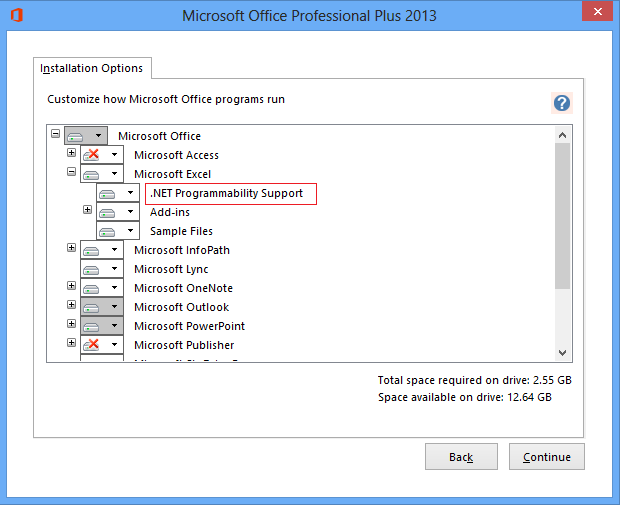
2. Then you will find the interop assemblies in the Windows Global Assembly Cache, specifically the folder: C:\Windows\assembly\GAC_MSIL\Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel\
This is a hidden protected system folder which won't show up in an ordinary hard drive search. If you try to go to "C:\Windows\assembly" Windows recognizes this as a special folder and will show you the full contents of the GAC in a flattened list instead of the individual folders that make up the GAC.