External Log File
I would like to save the test execution log to an external file on disk.
Solution
Overwrite the OnAfterTestCompleted method for individual tests in order to perform logic on Test Results. See our KB article on Executing Custom Scripts Before/After your Test Run for more information.
You can generate a custom log file by using the TestResult class. Write code in the code-behind file of your test (outside of a coded step). Here's how the placement looks:
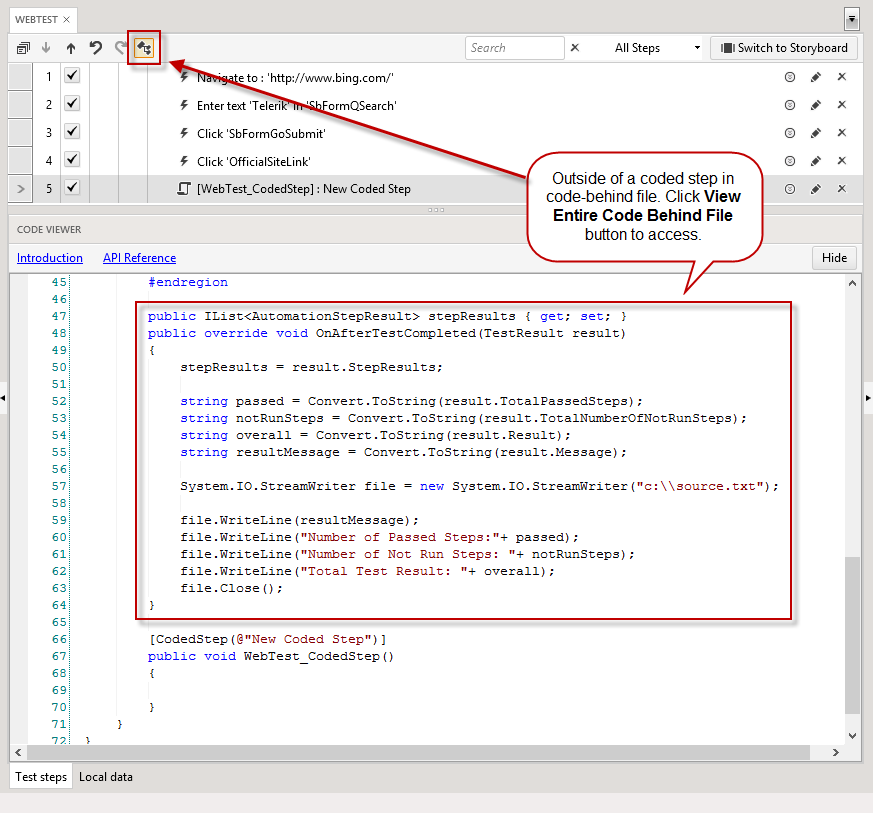
We have code samples for two file types:
Text File
public IList<AutomationStepResult> stepResults { get; set; }
public override void OnAfterTestCompleted(TestResult result)
{
stepResults = result.StepResults;
string passed = Convert.ToString(result.TotalPassedSteps);
string notRunSteps = Convert.ToString(result.TotalNumberOfNotRunSteps);
string overall = Convert.ToString(result.Result);
string resultMessage = Convert.ToString(result.Message);
System.IO.StreamWriter file = new System.IO.StreamWriter("c:\\source.txt");
file.WriteLine(resultMessage);
file.WriteLine("Number of Passed Steps:"+ passed);
file.WriteLine("Number of Not Run Steps: "+ notRunSteps);
file.WriteLine("Total Test Result: "+ overall);
file.Close();
}
Public Property stepResults() As IList(Of AutomationStepResult)
Get
Return m_stepResults
End Get
Set
m_stepResults = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_stepResults As IList(Of AutomationStepResult)
Public Overrides Sub OnAfterTestCompleted(result As TestResult)
stepResults = result.StepResults
Dim passed As String = Convert.ToString(result.TotalPassedSteps)
Dim notRunSteps As String = Convert.ToString(result.TotalNumberOfNotRunSteps)
Dim overall As String = Convert.ToString(result.Result)
Dim resultMessage As String = Convert.ToString(result.Message)
Dim file As New System.IO.StreamWriter("c:\source.txt")
file.WriteLine(resultMessage)
file.WriteLine("Number of Passed Steps:" & passed)
file.WriteLine("Number of Not Run Steps: " & notRunSteps)
file.WriteLine("Total Test Result: " & overall)
file.Close()
End Sub
Finally you'll need to Add an Assembly Reference for ArtOfTest.Common.Design. If it is already present, remove it and add it again. Add it from the *Test Studio\Bin* directory:
- C:\Program Files (x86)\Progress\Test Studio\Bin
Excel File
You'll need to add a reference to Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.dll. If it isn't already on your machine, ensure you download the version from Microsoft that matches your Office suite.
You'll need to create the Excel file on disk first.
public override void OnAfterTestCompleted(TestResult result)
{
string passed = Convert.ToString(result.TotalPassedSteps);
string notRunSteps = Convert.ToString(result.TotalNumberOfNotRunSteps);
string overall = Convert.ToString(result.Result);
string resultMessage = Convert.ToString(result.Message);
string [] split = resultMessage.Split(new Char [] {'\n'});
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excelApp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
string myPath = "C:\\Excel.xlsx";
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook workbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(myPath);
int idx = 1;
foreach (string s in split)
{
excelApp.Cells[idx, 1] = s;
idx++;
}
excelApp.Cells[idx + 1, 1] = ("Number of Passed Steps: " + passed);
excelApp.Cells[idx + 2, 1] = ("Number of Not Run Steps: " + notRunSteps);
excelApp.Cells[idx + 3, 1] = ("Total Test Result: " + overall);
excelApp.Visible = true;
excelApp.ActiveWorkbook.Save();
workbook.Close(false, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
excelApp.Workbooks.Close();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(workbook);
excelApp.Quit();
GC.Collect();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelApp);
}
Public Overrides Sub OnAfterTestCompleted(result As TestResult)
Dim passed As String = Convert.ToString(result.TotalPassedSteps)
Dim notRunSteps As String = Convert.ToString(result.TotalNumberOfNotRunSteps)
Dim overall As String = Convert.ToString(result.Result)
Dim resultMessage As String = Convert.ToString(result.Message)
Dim split As String() = resultMessage.Split(New [Char]() {ControlChars.Lf})
Dim excelApp As New Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application()
Dim myPath As String = "C:\Excel.xlsx"
Dim workbook As Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(myPath)
Dim idx As Integer = 1
For Each s As String In split
excelApp.Cells(idx, 1) = s
idx += 1
Next
excelApp.Cells(idx + 1, 1) = ("Number of Passed Steps: " + passed)
excelApp.Cells(idx + 2, 1) = ("Number of Not Run Steps: " + notRunSteps)
excelApp.Cells(idx + 3, 1) = ("Total Test Result: " + overall)
excelApp.Visible = True
excelApp.ActiveWorkbook.Save()
workbook.Close(False, Type.Missing, Type.Missing)
excelApp.Workbooks.Close()
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(workbook)
excelApp.Quit()
GC.Collect()
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelApp)
End Sub
How to find and use Office PIA's without Visual Studio installed
1. Make sure that during the installation of Microsoft Office .NET Programmability Support was selected.
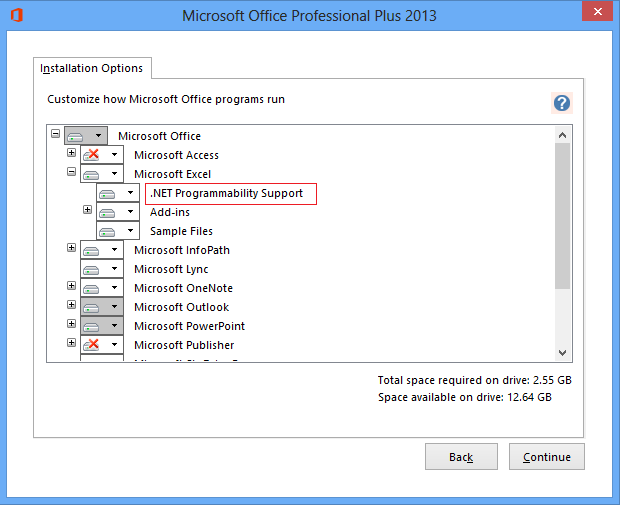
2. Then you will find the interop assemblies in the Windows Global Assembly Cache, specifically the folder: C:\Windows\assembly\GAC_MSIL\Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel\
This is a hidden protected system folder which won't show up in an ordinary hard drive search. If you try to go to "C:\Windows\assembly" Windows recognizes this as a special folder and will show you the full contents of the GAC in a flattened list instead of the individual folders that make up the GAC.