Table Overview
The Table class helps you easily create tabular data content. All you need to do is define the table content and pass a Table instance to a FixedContentEditor or a RadFixedDocumentEditor. From then on, these editors are responsible for positioning, measuring, drawing and splitting the table onto pages.
The Table is part of Telerik Document Processing, a
professional grade .NET library for creating and manipulating PDF, Word, XLSX and HTML files. To try it out sign up for a free 30-day trial.
This article aims to present the table-related API in RadPdfProcessing. It contains the following sections:
Defining Table Content
Each table contains a series of TableRow instances each of which contains a series of TableCell instances. In order to define a simple table, you need to generate the table cells and add some content to them.
Example 1 shows how to generate a simple table with two rows and three columns with some sample text in each table cell.
[C#] Example 1: Create simple table
Table table = new Table();
TableRow firstRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell11");
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell12");
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell13");
TableRow secondRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell21");
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell22");
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell23");
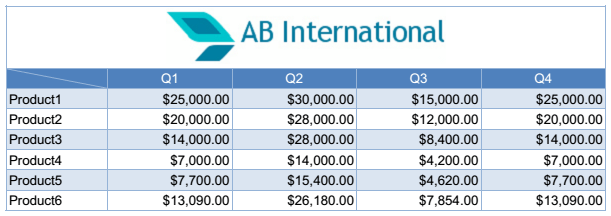
The result table is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Table
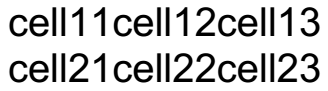
Using DefaultCellProperties
If you want to apply default styling to all the cells in a table, you can use Table's DefaultCellProperties property. This allows to easily modify the default cell presentation.
- Padding: Specifies the distances between the inner cell border contour and the cell content.
- Borders: Property of type TableCellBorders, which specifies the borders of a single cell. The available borders are left, right, top, bottom, diagonal up and diagonal down.
- Background: Specifies the background of the cell.
Example 2 shows how to use the DefaultCellProperties of a table
[C#] Example 2: Use DefaultCellProperties of Table
Table table = new Table();
Border redBorder = new Border(2, new RgbColor(255, 0, 0));
table.DefaultCellProperties.Borders = new TableCellBorders(redBorder);
table.DefaultCellProperties.Padding = new Thickness(20, 10, 20, 10);
table.DefaultCellProperties.Background = new RgbColor(0, 255, 0);
TableRow firstRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
TableRow secondRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
The result of the snippet in Example 2 is demonstrated on Figure 2.
Figure 2: Result of DefaultCellProperties modification
Modifying a Table
There are several factors that affect tables measuring calculations. Some of them are listed and explained bellow:
Margin: Specifies the distances between the table borders outline and the rest of the document's content.
Padding: Set through the TableCell's Padding property, it specifies the distances between cell borders inner contour and the cell content.
-
LayoutType: Specifies the algorithm, which shall be used to layout table contents. There are two options available in the TableLayoutType enumeration:
- AutoFit – The table width fits the content unless the needed width is bigger than the available measuring width.
- FixedWidth – The table width always fits the available measuring width.
HorizontalAlignment: Specifies the alignment of the table inside the page.
BorderSpacing: Specifies the distance between all the borders in the table. This distance is measured differently depending on the BorderCollapse option.
-
BorderCollapse: Specifies the way the border spacing calculations should be done. There are two options:
- Collapse: The distance between borders is measured from the middle lines of the borders
- Separate: The distance between borders is measured from the outer border contour.
Example 3 demonstrates how border calculations occur with different BorderCollapse option. The code in this example creates an empty table and sets default cell padding and red table border with thickness 10 to it.
[C#] Example 3: Create table with red border
Table table = new Table();
table.DefaultCellProperties.Padding = new Thickness(10, 6, 10, 6);
Border redBorder = new Border(10, new RgbColor(255, 0, 0));
table.Borders = new TableBorders(redBorder);
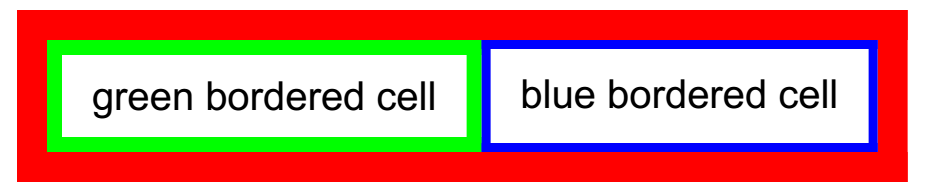
Example 4 adds a single row with two cells to the table from Example 3. The first cell has a green border with thickness 5 while the second cell has a blue border with thickness 3.
[C#] Example 4: Add green and blue cells
TableRow tableRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
TableCell firstCell = tableRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
Border greenBorder = new Border(5, new RgbColor(0, 255, 0));
firstCell.Borders = new TableCellBorders(greenBorder, greenBorder, greenBorder, greenBorder);
firstCell.Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("green bordered cell");
TableCell secondCell = tableRow.Cells.AddTableCell();
Border blueBorder = new Border(3, new RgbColor(0, 0, 255));
secondCell.Borders = new TableCellBorders(blueBorder, blueBorder, blueBorder, blueBorder);
secondCell.Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("blue bordered cell");
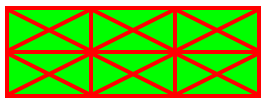
Figure 3 shows the table from Example 3 and 4 with BorderCollapse property set to Collapse - all borders are drawn so that their middle lines coincide.
[C#] Example 5: Collapse border
table.BorderCollapse = BorderCollapse.Collapse;
Figure 3: Collapsed border
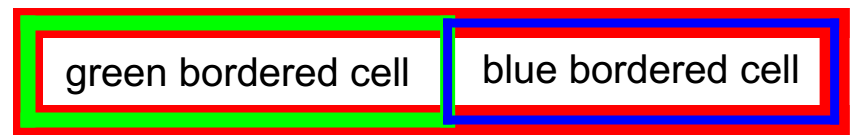
Figure 4 shows the same table with BorderCollapse property set to Separate - all borders are drawn so that their outer contour coincide.
[C#] Example 6: Separate border
table.BorderCollapse = BorderCollapse.Separate;
Figure 4: Separated border
Drawing Table with RadFixedDocumentEditor
When a table is generated, it could be inserted in the PDF document using the RadFixedDocumentEditor's InsertTable() method. This way the table is inserted in the document and split onto pages if necessary.
Example 7 generates a simple table with two cells.
[C#] Example 7: Create table
Table table = new Table();
Border border = new Border();
table.Borders = new TableBorders(border);
table.DefaultCellProperties.Borders = new TableCellBorders(border, border, border, border);
table.BorderSpacing = 5;
table.BorderCollapse = BorderCollapse.Separate;
TableRow row = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
row.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("First cell");
row.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("Second cell");
Example 8 inserts the table from Example 7 in a RadFixedDocumentEditor and specifies the table layout type to AutoFit.
[C#] Example 8: Insert AutoFit table
using (RadFixedDocumentEditor editor = new RadFixedDocumentEditor(document))
{
table.LayoutType = TableLayoutType.AutoFit;
editor.InsertTable(table);
}
The result is that the table width is exactly as needed for fitting the cells content as visible in Figure 5.
Figure 5: AutoFit table

Specifying FixedWidth layout option produces different results.
[C#] Example 9: Insert FixedWidth table
using (RadFixedDocumentEditor editor = new RadFixedDocumentEditor(document))
{
table.LayoutType = TableLayoutType.FixedWidth;
editor.InsertTable(table);
}
Figure 6: FixedWidth table

Drawing Table with FixedContentEditor
When in need of more customization options, you can use the DrawTable() method of FixedContentEditor instead of RadFixedDocumentEditor.
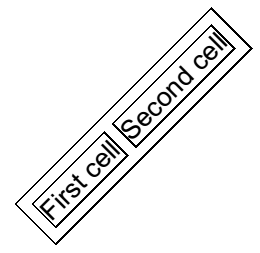
Example 10 shows how to draw a rotated table with the help of FixedContentEditor.
[C#] Example 10: Draw rotated table
Table table = new Table();
TableRow firstRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell11");
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell12");
firstRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell13");
TableRow secondRow = table.Rows.AddTableRow();
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell21");
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell22");
secondRow.Cells.AddTableCell().Blocks.AddBlock().InsertText("cell23");
RadFixedDocument document = new RadFixedDocument();
RadFixedPage page = document.Pages.AddPage();
FixedContentEditor editor = new FixedContentEditor(page, new SimplePosition());
editor.Position.Translate(10, 100);
editor.Position.Rotate(-45);
editor.DrawTable(table);
As a result, on Figure 7 you can see a 45-degree rotated table similar to the one on Figure 5.
Figure 7: FixedWidth table
Supported Border Styles
As of Q3 2024, along with the BorderStyle.Single, RadPdfProcessing offers Dotted, Dashed, and DashSmallGap border styles. With this update, the Dotted, Dashed, DashSmallGap, and Thick border lines are now exported from RadFlowDocument to RadFixedDocument as well.
| BorderStyle | Border Design |
|---|---|
| Single |  |
| Dotted |  |
| Dashed |  |
| DashSmallGap |  |
See Also
- FixedContentEditor
- RadFixedDocumentEditor
- TableRow
- TableCell
- How to Generate a Table with Images with PdfProcessing
- Creating Custom Layout Tables with RadPdfProcessing
- Implementing Column Span in RadPdfProcessing Tables
- Generating a Table with RadFixedDocumentEditor
- Avoiding Table Splits Across Pages Using FixedContentEditor in RadPdfProcessing
- How to Achieve Alternating Row Color for Tables in PdfProcessing