Virtualization
The Kendo UI AutoComplete, the ComboBox, the DropDownList, and the MultiSelect support UI and data virtualization.
Virtualization enables you to display large datasets by using a fixed amount of list items in the popup list of the ComboBox regardless of the dataset size. When the list is scrolled, the ComboBox reuses the existing items to display the relevant data instead of creating new ones.
The approaches for configuring the virtualization functionality of the ComboBox that are demonstrated in this article are identical for configuring the grouping functionality of the AutoComplete, DropDownList, and MultiSelect components.
For runnable examples on virtualization, refer to the following demos:
- Virtualization in the ComboBox (demo)
- Virtualization in the AutoComplete (demo)
- Virtualization in the DropDownList (demo)
- Virtualization in the MultiSelect (demo)
Getting Started
To retrieve and display only a subset of the whole dataset, the ComboBox combines data and User Interface (UI) virtualization. To implement data virtualization, the ComboBox uses the paging functionality of the DataSource and remote data retrieval. In this way, the component retrieves only a specified data page instead of requesting the whole dataset at once. To ensure the proper functioning of the ComboBox, configure the paging of the DataSource correctly. For more information, refer to the server paging configuration.
The following example demonstrates how to set the minimum component and DataSource configurations for the virtualization to work as expected.
<input id="orders" style="width: 400px" />
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#orders").kendoComboBox({
template: '#= OrderID # | #= ShipName #',
dataTextField: "ShipName",
dataValueField: "OrderID",
filter: "contains",
virtual: {
itemHeight: 26,
valueMapper: function(options) {
$.ajax({
url: "https://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/service/Orders/ValueMapper",
type: "GET",
dataType: "jsonp",
data: convertValues(options.value),
success: function (data) {
options.success(data);
}
})
}
},
height: 520,
dataSource: {
type: "odata",
transport: {
read: "https://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/service/Northwind.svc/Orders"
},
pageSize: 80,
serverPaging: true,
serverFiltering: true
}
});
});
// This is a helper method that serializes values into a understandable format for the server.
// This method is not obligatory to use. Instead, you need to send the value in a format that is understandable for the server.
function convertValues(value) {
var data = {};
value = $.isArray(value) ? value : [value];
for (var idx = 0; idx < value.length; idx++) {
data["values[" + idx + "]"] = value[idx];
}
return data;
}
</script>Basic Configuration
In order for the virtualization to properly work:
Setting the Item and Container Heights
The ComboBox applies a specific strategy of reusing a list of DOM elements for displaying the corresponding data chunk. The number of these elements is determined based on the height and itemHeight options. Once the number is calculated, the component creates those elements and starts reusing them to display the current data source page.
All items in the virtualized list need to have the same height. If you do not specify a height value, itemHeight will be automatically set as it is set in the current theme and font size.
If you do not specify an
itemHeightoption, the ComboBox will perform an extra DataSource request which rarely causes any critical issues.
The virtualized list container needs to have a height option that is set in pixels. Otherwise, the list will use the default height of 200px.
Setting the Page Size
To ensure the correct work of the ComboBox, the pageSize value of the DataSource is calculated automatically based on the ((height / itemHeight) * 4) formula. The ComboBox itself does the calculation and the defined pageSize value is overridden if it does not match the calculated one. For example, if the height is set to 520px and the itemHeight is set to 26, the pageSize will be set to 80 because ((520 / 26) * 4) is equal to 80.
- Enabling paging and setting
pageSizeis efficient only when the virtualization of the ComboBox is configured.- To avoid multiple initial requests, define a correct
pageSizevalue.
Returning the Appropriate Data
The response for each virtualization request has to contain the following fields:
- An array with the specified page of data.
- The total count of all items that are present in the dataset of the
Totalfield.
You can specify the fields that contain the array of data and the total in the configuration of the data source schema of the ComboBox. Once a page of data is received on the client, it will be cached, and if the user scrolls through the list, no new requests will be made for earlier pages of data and the virtualization will happen on the client only.
To prevent infinite requests for the last page of data, ensure that the
Totalcount is reached. If it is not, the component will make requests until it receives the denoted total amount of unique items.
Value Mapping
As of the Kendo UI R3 2016 release, the implementation of the
valueMapperfunction is optional and is required only if the component contains an initial value or uses thevaluemethod.
Unlike the data and UI virtualization, the valueMapper was introduced because the ComboBox needs to maintain the selected item and to display the selected data item based on the value alone. To display the selected text, the component has to retrieve the selected data item which is part of a specific data page that is unknown to you. The required information is gathered with the valueMapper callback. It passes the selected value and requests the corresponding row index or dataItem of that value depending on the mapValueTo configuration option.
Mapping index Values
When the component receives a value which is not fetched from the remote server yet, it calls the valueMapper function and passes the selected values in that function. If the mapValueTo is not explicitly set to dataItem, the valueMapper implementation is expected to return the respective data item index. From this index the component calculates the page number and in this way pre-fetches only that particular page by sending an additional Ajax request. If the value does not exist, the valueMapper is expected to return null, [], or -1 and the component will deselect the currently selected items.
valueMapper: function(options) {
$.ajax({
url: "https://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/service/Orders/ValueMapper",
type: "GET",
data: options.value, //send value to the server
success: function (data) {
options.success(data); //return the index number of the corresponding data item
}
})
}Mapping dataItem Values
The changes introduced with the Kendo UI R3 2016 release enable you to determine if the valueMapper must resolve a value to an index or a value to a dataItem. This is configured through the mapValueTo option that accepts two possible values—"index" or "dataItem". By default, the mapValueTo is set to "index", which does not affect the current behavior of the virtualization process.
If you implement the mapValueTo: "dataItem" configuration, the valueMapper is expected to return the dataItems that corresponds to the selected values. The component will use the returned dataItems to render the selected values but will not scroll the list to the selected values. When the user opens the list, the component will display the options from the first data page instead, no matter whether the selected value is a part of the first page or not. This is the main limitation of the mapValueTo: dataItem configuration.
mapValueTo: "dataItem",
valueMapper: function(options) {
$.ajax({
url: "https://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/service/Orders/ValueMapper",
type: "GET",
data: options.value, //send value to the server
success: function (dataItems) {
options.success(dataItems); //return the dataItems that correspond to provided values
}
})
}Mapping Values to index
The mapValueTo: "index" configuration is set by default. The valueMapper is called when you want to select a data item that is not present in the data source.
To see the process in action, use the sample case with the following component configuration:
- The
pageSizeis set to50. - The selected value is
foo.
On initial load, the component checks whether the selected value is present in the loaded data. If it is not, it performs the following actions:
- It calls the
valueMapper, requesting a row index that corresponds to the selected valuefoo. - The
valueMappercalls theservice 1, passing the selected valuefooto it. - The
service 1finds the row index that corresponds to thefoovalue. In this case it is1250. - The
valueMapperfunction returns this row index to the component. - The component calculates the page number. In this case it is
25. - The component requests it from the
service 2using thedataSource. - The
service 2returns the corresponding 25th page. - The
dataSourcechanges the page to25and displays the items showing the selected item too.

Function result The valueMapper is expected to return a row index or a list of indices when a multiple selection is available. That being said, the service is expected to return either an index (number) or a list of indices. If the value does not exist, the valueMapper returns null, [], or -1, and the component deselects the currently selected items. For an example, refer to the result of the test service that is used in the online demos.
$.ajax({
url: "https://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/service/Orders/ValueMapper",
type: "GET",
dataType: "jsonp",
data: { "values[0]": "10661" }
success: function (data) {
// The returned data is [413].
options.success(data);
}
})The Ajax method calls URLs similar to https://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/service/Orders/ValueMapper?values[0]=10661 and the result is callback([413]) //the result is JSONP.
Function implementation The service maps the selected value to a particular row index. The implementation of this functionality is completely under your control. However, the most simplified implementation includes the iteration of all items counting the index of the rows. A more optimized solution still is to use a dedicated SQL method that handles this action internally. You can do this by using the ROW_NUMBER() function.
Mapping Values to dataItem
The mapValueTo: "dataItem" configuration is available as of the Kendo UI R3 2016. The valueMapper is called when you want to select a data item that is not present in the data source.
To see the process in action, use the sample case with the following component configuration:
- The
pageSizeis set to50. - The selected value is
foo.
On initial load, the component checks whether the selected value is present in the loaded data. If it is not, it performs the following actions:
- It calls the
valueMapper, requesting a dataItem that corresponds to the selected valuefoo. - The
valueMappercalls theservice 1, passing the selected valuefooto it. - The
service 1finds the dataItem that corresponds to thefoovalue. In this case it is{text: "bar", value: "foo"}. - The
valueMapperfunction returns this dataItem to the component. - The component renders the selected item template.
- The component requests the first page from
service 2using thedataSource. - The
service 2returns the first data page. - The component list displays the items from the first page no matter if the selected items are part of it or not.
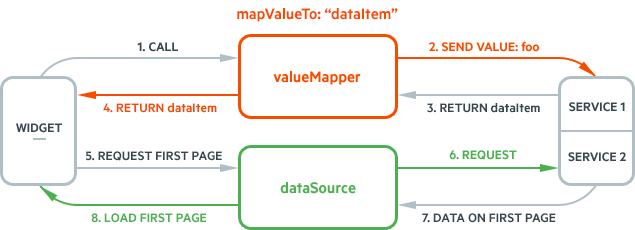
Function result The valueMapper is expected to return a data item or a list of data items when a multiple selection is available. That being said, the service is expected to return either an data item (object) or a list of data items. If the values does not exist, the valueMapper returns null or [], and the component deselects the currently selected values.
Known Limitations
- The virtualization feature can work with objects, while virtualization of primitive values is not supported.
- The rendered items should have equal heights. Every single item in the virtualized list displays a height that is set through the
itemHeightoption. - The virtualization feature performs a complex data pre-fetching and assumes that the DataSource state will not change without the knowledge of the component. Any manual data operations, such as
read,page,filter,add,remove, etc., might lead to unexpected behavior for the component and are not supported.