Row behaviors
RadGridView manages user mouse and keyboard input over its rows by GridRowBehavior. Depending on the row type, RadGridView introduces different behaviors, listed on the table below:
| Row behavior | Row type |
|---|---|
| GridDataRowBehavior | GridViewDataRowInfo |
| GridHierarchyRowBehavior | GridViewHierarchyRowInfo |
| GridNewRowBehavior | GridViewNewRowInfo |
| GridGroupRowBehavior | GridViewGroupRowInfo |
| GridFilterRowBehavior | GridViewFilteringRowInfo |
| GridHeaderRowBehavior | GridViewTableHeaderRowInfo |
| GridDetailViewRowBehavior | GridViewDetailsRowInfo |
By implementing a specific custom row behavior, developers can change the default row functionality or supplement the existing one.
Let’s start with constructing a hierarchical RadGridView and populate it with data.
public RowBehaviorsForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
//Fill data
DataTable items = new DataTable("Items");
items.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(int));
items.Columns.Add("Title", typeof(string));
items.Columns.Add("IsActive", typeof(bool));
DataTable subItems = new DataTable("SubItems");
subItems.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(int));
subItems.Columns.Add("Name", typeof(string));
subItems.Columns.Add("ItemId", typeof(int));
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
items.Rows.Add(i, "Item" + i, i % 2 == 0);
for (int j = 1000; j <= 1005; j++)
{
subItems.Rows.Add(j, "SubItem" + j, i);
}
}
//Set up grid hierarchy
radGridView1.DataSource = items;
radGridView1.AutoSizeColumnsMode = GridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill;
GridViewTemplate template = new GridViewTemplate();
template.ReadOnly = true;
template.AutoSizeColumnsMode = GridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill;
GridViewRelation relation = new GridViewRelation(radGridView1.MasterTemplate, template);
relation.ParentColumnNames.Add("Id");
relation.ChildColumnNames.Add("ItemId");
radGridView1.MasterTemplate.Templates.Add(template);
radGridView1.Relations.Add(relation);
template.ReadOnly = false;
template.DataSource = subItems;
}
Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
'Fill data
Dim items As New DataTable("Items")
items.Columns.Add("Id", GetType(Integer))
items.Columns.Add("Title", GetType(String))
items.Columns.Add("IsActive", GetType(Boolean))
Dim subItems As New DataTable("SubItems")
subItems.Columns.Add("Id", GetType(Integer))
subItems.Columns.Add("Name", GetType(String))
subItems.Columns.Add("ItemId", GetType(Integer))
For i As Integer = 1 To 3
items.Rows.Add(i, "Item" & i, i Mod 2 = 0)
For j As Integer = 1000 To 1005
subItems.Rows.Add(j, "SubItem" & j, i)
Next
Next
'Set up grid hierarchy
RadGridView1.DataSource = items
RadGridView1.AutoSizeColumnsMode = GridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill
Dim template As New GridViewTemplate()
template.[ReadOnly] = True
template.AutoSizeColumnsMode = GridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill
Dim relation As New GridViewRelation(RadGridView1.MasterTemplate, template)
relation.ParentColumnNames.Add("Id")
relation.ChildColumnNames.Add("ItemId")
RadGridView1.MasterTemplate.Templates.Add(template)
RadGridView1.Relations.Add(relation)
template.[ReadOnly] = False
template.DataSource = subItems
End Sub
By default, when the user hits the Delete key over a certain row, the row is deleted. We will extend this functionality by notifying the user when he tries to delete a parent row, which ChildRows collection is not empty. For this purpose, it is necessary to create a custom grid behavior. To do this, create a new class named CustomGridHierarchyRowBehavior. As we are currently using a hierarchical grid, our class should inherit the GridHierarchyRowBehavior. Override the ProcessDeleteKey method in order to display a MessageBox and proceed with the delete operation after confirmation only: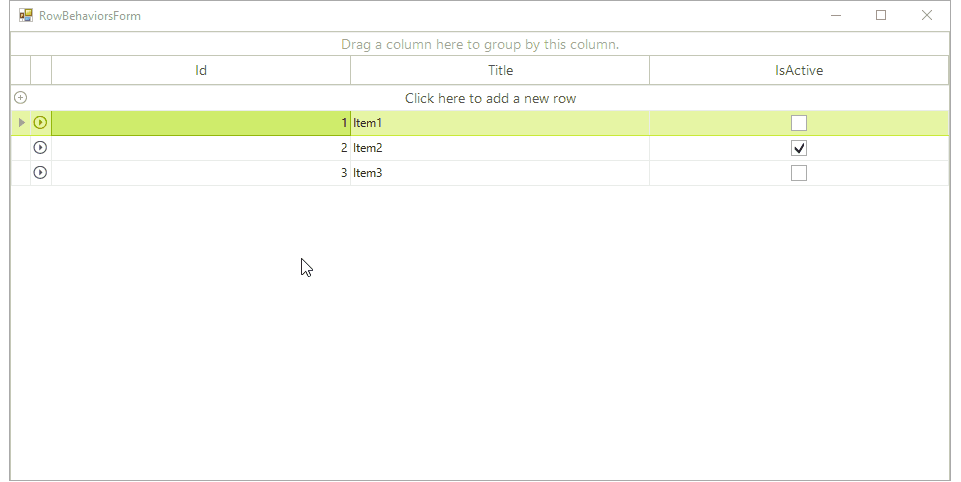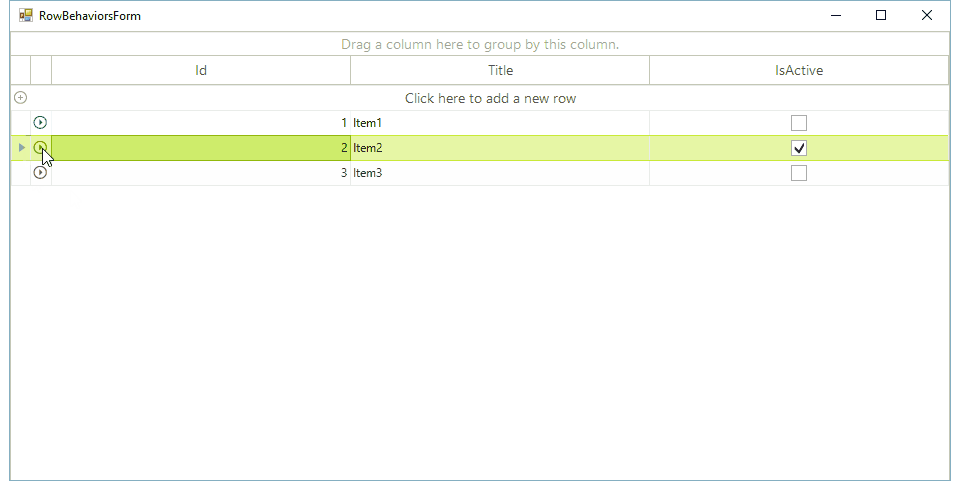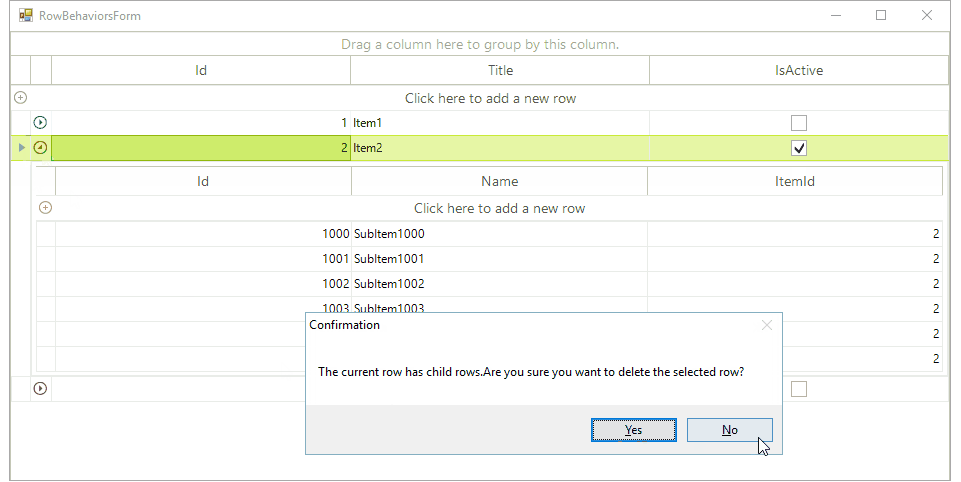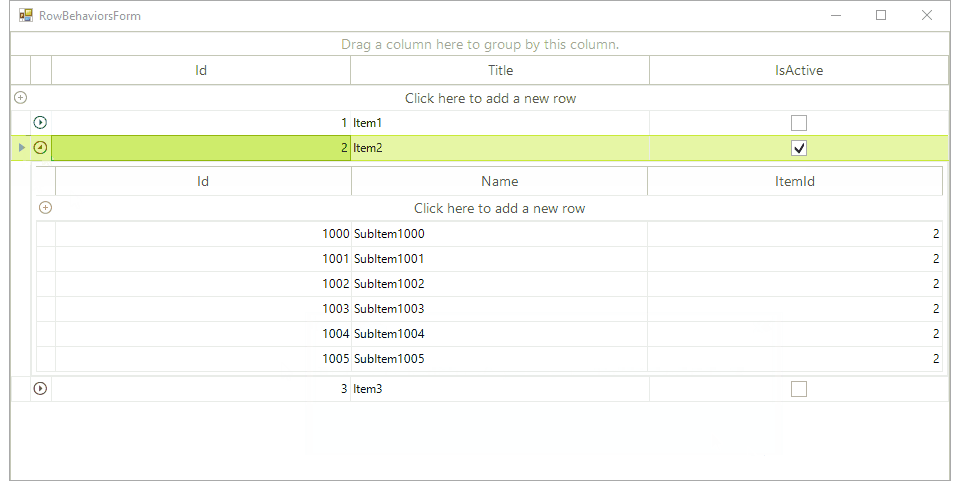
public class CustomGridHierarchyRowBehavior : GridHierarchyRowBehavior
{
protected override bool ProcessDeleteKey(KeyEventArgs keys)
{
if (this.GridControl.CurrentRow.ChildRows.Count > 0)
{
DialogResult result = MessageBox.Show("The current row has child rows." +
"Are you sure you want to delete the selected row?", "Confirmation", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo);
if (result == DialogResult.No)
{
return true;
}
}
return base.ProcessDeleteKey(keys);
}
}
Public Class CustomGridHierarchyRowBehavior
Inherits GridHierarchyRowBehavior
Protected Overrides Function ProcessDeleteKey(keys As KeyEventArgs) As Boolean
If Me.GridControl.CurrentRow.ChildRows.Count > 0 Then
Dim result As DialogResult = MessageBox.Show("The current row has child rows." & "Are you sure you want to delete the selected row?", "Confirmation", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo)
If result = DialogResult.No Then
Return True
End If
End If
Return MyBase.ProcessDeleteKey(keys)
End Function
End Class
Next we will register this behavior in our grid. Add the following code after populating the grid with data:
//register the custom row behavior
BaseGridBehavior gridBehavior = radGridView1.GridBehavior as BaseGridBehavior;
gridBehavior.UnregisterBehavior(typeof(GridViewHierarchyRowInfo));
gridBehavior.RegisterBehavior(typeof(GridViewHierarchyRowInfo), new CustomGridHierarchyRowBehavior());
'register the custom row behavior
Dim gridBehavior As BaseGridBehavior = TryCast(RadGridView1.GridBehavior, BaseGridBehavior)
gridBehavior.UnregisterBehavior(GetType(GridViewHierarchyRowInfo))
gridBehavior.RegisterBehavior(GetType(GridViewHierarchyRowInfo), New CustomGridHierarchyRowBehavior())
The next modification we are going to introduce is to override the OnMouseDownLeft method and show the context menu for the GridCheckBoxCellElement, associated with the mouse location. First, it is necessary to use the grid navigator to process selection of the cell element, positioned at the mouse location. Afterwards, show the context menu for the specific cell:
protected override bool OnMouseDownLeft(MouseEventArgs e)
{
GridCellElement cellElement = this.GetCellAtPoint(e.Location);
if (cellElement != null && cellElement is GridCheckBoxCellElement)
{
GridRowElement rowElement = cellElement.RowElement;
this.Navigator.BeginSelection(this.GetMouseNavigationContext(e));
this.Navigator.Select(rowElement.RowInfo, cellElement.ColumnInfo);
this.Navigator.EndSelection();
if (!cellElement.IsInValidState(true))
{
cellElement = this.GetCellAtPoint(e.Location);
}
if (cellElement != null)
{
GridViewElement.ContextMenuManager.ShowContextMenu(cellElement);
}
return true;
}
return base.OnMouseDownLeft(e);
}
Protected Overrides Function OnMouseDownLeft(e As MouseEventArgs) As Boolean
Dim cellElement As GridCellElement = Me.GetCellAtPoint(e.Location)
If cellElement IsNot Nothing AndAlso TypeOf cellElement Is GridCheckBoxCellElement Then
Dim rowElement As GridRowElement = cellElement.RowElement
Me.Navigator.BeginSelection(Me.GetMouseNavigationContext(e))
Me.Navigator.[Select](rowElement.RowInfo, cellElement.ColumnInfo)
Me.Navigator.EndSelection()
If Not cellElement.IsInValidState(True) Then
cellElement = Me.GetCellAtPoint(e.Location)
End If
If cellElement IsNot Nothing Then
GridViewElement.ContextMenuManager.ShowContextMenu(cellElement)
End If
Return True
End If
Return MyBase.OnMouseDownLeft(e)
End Function
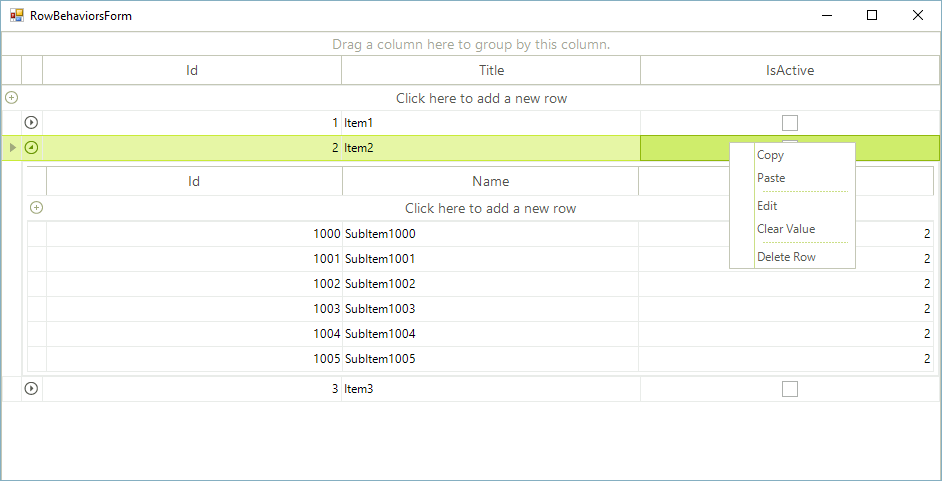
RadGridView supports rows/cells navigation by default, using the arrow keys. It is possible to customize this behavior as well. In the CustomGridHierarchyRowBehavior class override the ProcessKey method and stop the base grid logic for navigation upwards/downwards if the current row belongs to the MasterTemplate and its “IsActive” cell value is set to false:
public override bool ProcessKey(KeyEventArgs keys)
{
if (keys.KeyCode == Keys.Up || keys.KeyCode == Keys.Down)
{
DataRowView rowView = this.GridControl.CurrentRow.DataBoundItem as DataRowView;
if (rowView != null && this.GridControl.CurrentRow.ViewTemplate == this.MasterTemplate)
{
if ((bool)rowView.Row["IsActive"] == false)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return base.ProcessKey(keys);
}
Public Overrides Function ProcessKey(keys__1 As KeyEventArgs) As Boolean
If keys__1.KeyCode = Keys.Up OrElse keys__1.KeyCode = Keys.Down Then
Dim rowView As DataRowView = TryCast(Me.GridControl.CurrentRow.DataBoundItem, DataRowView)
If rowView IsNot Nothing AndAlso Me.GridControl.CurrentRow.ViewTemplate.Equals(Me.MasterTemplate) Then
If CBool(rowView.Row("IsActive")) = False Then
Return True
End If
End If
End If
Return MyBase.ProcessKey(keys__1)
End Function
Following the demonstrated approach, developers can customize not only the hierarchy rows, but the new row for example, implementing a custom GridNewRowBehavior and registering it for the GridViewNewRowInfo.