Binding to Array and ArrayList
The examples below demonstrate binding to a generic list, an arrays of custom objects, and an ArrayList of custom objects. This collections have limitations when used as a data source in which case a BindingList must be used.
Note: BindingList is the preferred collection since its changes are automatically reflected on the data-bound control.
Binding to a Array List
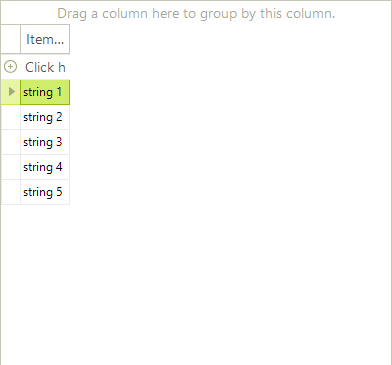
The example below creates an ArrayList of generic objects initialized with five values and assigned as a DataSource to the RadGridView.
public class ValueType<T>
{
T item;
public ValueType() { }
public ValueType(T item)
{
this.item = item;
}
public T ItemProperty
{
get { return this.item; }
set { this.item = value; }
}
}
Public Class ValueType(Of T)
Private item As T
Public Sub New()
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal item As T)
Me.item = item
End Sub
Public Property ItemProperty() As T
Get
Return Me.item
End Get
Set(ByVal value As T)
Me.item = value
End Set
End Property
End Class
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
list.Add(new ValueType<string>("string " + (i + 1).ToString()));
}
this.radGridView1.DataSource = list;
Dim list As New ArrayList()
Dim i As Integer = 0
While i < 5
list.Add(New ValueType(Of String)("string " + (i + 1).ToString()))
System.Math.Max(System.Threading.Interlocked.Increment(i), i - 1)
End While
Me.RadGridView1.DataSource = list
Binding to an Array of Objects
Arrays of objects containing bindable types can be bound to RadGridView by assigning the array to the DataSource property of the grid.
The example below defines a "MyObject" class containing one integer and one string property. The snippet of code at end of the example creates an array of MyObject, initializes the array with two objects and assigns the array to the DataSource. The MyObject class would typically be placed in its own separate class file and the array creation, initialization and assignment code might be placed in a form's Load event handler.

public class MyObject
{
public MyObject(int myInt, string myString)
{
_myInt = myInt;
_myString = myString;
}
private int _myInt;
public int MyInt
{
get { return _myInt; }
set { _myInt = value; }
}
private string _myString;
public string MyString
{
get { return _myString; }
set { _myString = value; }
}
}
Public Class MyObject
Public Sub New(ByVal myInt As Integer, ByVal myString As String)
_myInt = myInt
_myString = myString
End Sub
Private _myInt As Integer
Public Property MyInt() As Integer
Get
Return _myInt
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
_myInt = value
End Set
End Property
Private _myString As String
Public Property MyString() As String
Get
Return _myString
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
_myString = value
End Set
End Property
End Class
MyObject[] myArray = new MyObject[2] { new MyObject(1, "object one"), new MyObject(2, "object two") };
radGridView1.DataSource = myArray;
Dim myArray As MyObject() = New MyObject(1) {New MyObject(1, "object one"), New MyObject(2, "object two")}
RadGridView1.DataSource = myArray