Using the Execution Log
The execution log or test log is a log available after test failure in the test view or as part of the step failure details. You can pull it out by clicking View Log button
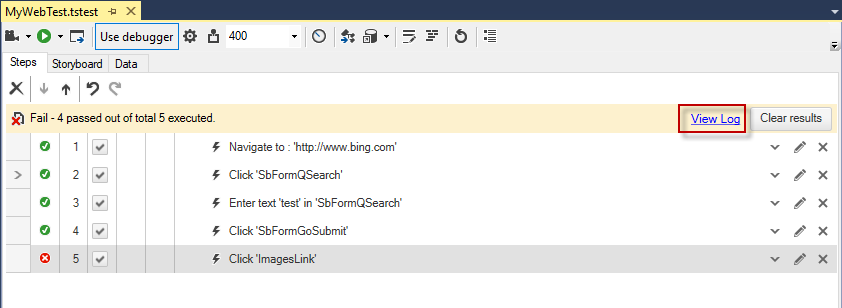
or from failure details:
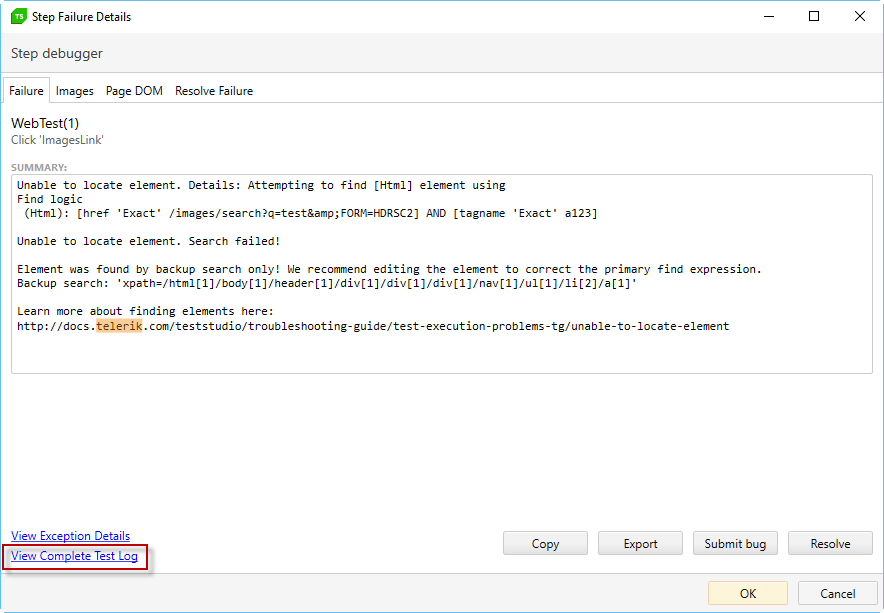
The execution log is a record of the steps executed in the test, whether they passed or failed, and in case they failed, why. It records what actions a step takes and what elements it acts upon. It includes all steps in one sequence, regardless of whether they are part of the main parent test or a test as step.
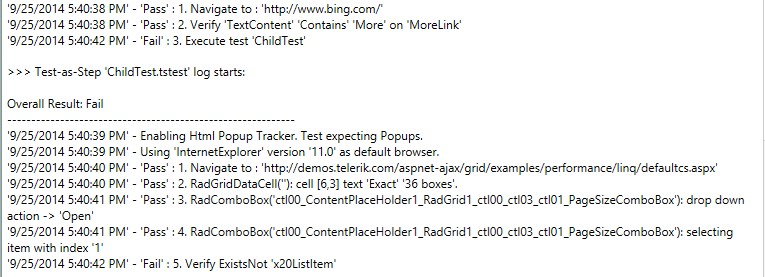
It says what errors arose in the case of a failure, giving detailed information on where the error occurred, and whether the error caused the test to fail.

The content of the Execution log can be directly copied to clipboard and pasted to any text editor for analyzing purposes.
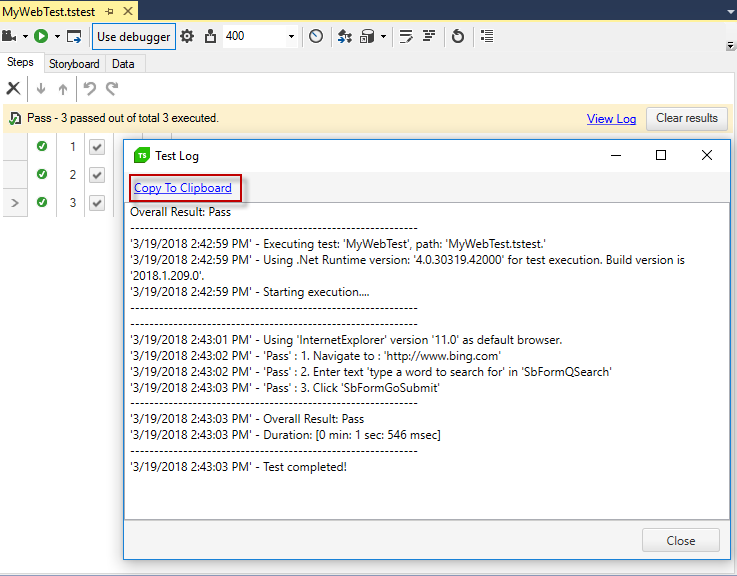
The execution log is an excellent resource for forming a clear story of what led to a failure for the below described scenarios.
When to export the Execution Log?
Anytime a test fails unexpectedly and without clear explanation, the execution log can help in determining the cause. This includes any of the following, when unexpected:
The test closes after waiting;
A step fails unexpectedly and the test continues;
The test fails without executing any steps;
Exporting The Execution Log.
In the Step Failure Details window, you can choose to export results to file, including the execution log.
What to look for in the Execution Log?
The Execution Log lists four main types of information. Two of these, the action taken by the step and the element acted upon by the step, are included in the Test view. However, they can still be useful if the recipient of the execution log does not have access to the associated test (for example, the Test Studio Dev support team). The other two categories of information are step execution properties (including whether to continue on failure and whether to break on execution) and error information. Each of these pieces of information is contained elsewhere in Test Studio Dev, the Execution log provides a sequential summary of the entire test leading up to failure.