Model Binding and Strongly Typed Data Controls Support
Strongly Typed Data Controls Support
When template fields are used into the Telerik data bound controls for customizing templates and bound the field value the late-bound expressions are typically used. For example, below we are using the Eval() helper method to data-bind the "CategoryName" property from an objects which is bound to the RadGrid:
<telerik:GridTemplateColumn HeaderText="Category" UniqueName="CategoryID"
DataField="CategoryID" SortExpression="CategoryID">
<ItemTemplate>
<%# Eval("Category.CategoryName") %>
<ItemTemplate>
</telerik:GridTemplateColumn
When we perform two-way data-binding the Bind() method is used:
<telerik:GridTemplateColumn HeaderText="Category" UniqueName="CategoryID"
DataField="CategoryID" SortExpression="CategoryID">
<EditItemTemplate>
<telerik:RadComboBox RenderMode="Lightweight" Skin="Metro" ID="ComboBox1" runat="server" SelectMethod="GetCategories"
DataValueField="CategoryID" DataTextField="CategoryName"
SelectedValue='<%# Bind("CategoryID") %>'></telerik:RadComboBox>
</EditItemTemplate>
</telerik:GridTemplateColumn>
On the other side the .NET 4.5 provides ability to enable strongly-typed data templates. To enable them the ItemType property needs to be set on the data bound control. After setting it two new types will be generated in the scope of the control’s template: Item and BindItem.
Make sure that you set the ItemType property of RadGrid and the GridTableView containing the columns.
For example the code snippet above could be rewritten as:
<telerik:GridTemplateColumn HeaderText="Category" UniqueName="CategoryID"
DataField="CategoryID" SortExpression="CategoryID">
<ItemTemplate>
<%# Item.Category.CategoryName %>
</ItemTemplate>
<EditItemTemplate>
<telerik:RadComboBox RenderMode="Lightweight" Skin="Metro" ID="ComboBox1" runat="server" SelectMethod="GetCategories"
DataValueField="CategoryID" DataTextField="CategoryName" SelectedValue="<%# BindItem.CategoryID %>"></telerik:RadComboBox>
</EditItemTemplate>
</telerik:GridTemplateColumn>
The developers could use these variables in data-binding expressions and to get full intellisense support.
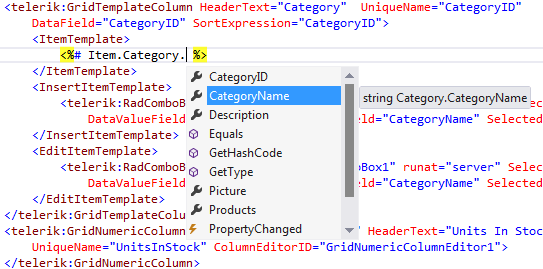
Due to the fact that the RadGrid control has GridTableView as a child control to have intellisense into grid’s columns you need to set the ItemType property of the MasterTableView.
Model Binding Selecting Data, Paging and Sorting
To bind databound UI controls via ModelBinding you need to set only the SelectMethod property to the name of the public method placed into the page's code-behind file:
<telerik:RadGrid RenderMode="Lightweight" ID="RadGrid1" GridLines="None" runat="server" AllowSorting="true" PageSize="10" AllowPaging="True" SelectMethod="GetProducts"
AutoGenerateColumns="False">
The GetProducts method has following declaration:
DataClassesDataContext context = new DataClassesDataContext();
public IQueryable<Employee> GetProducts()
{
return from e in context.Employees
select e;
}
Private con As New DataClassesDataContext()
Public Function GetProducts() As IQueryable(Of Employee)
Return From e In context.Employeese
End Function
Or it can be with parameters:
public IQueryable<Employee> GetProducts(string sortByExpression, int startRowIndex, int maximumRows, out int totalRowCount)
{
....
}
Public Function GetProducts(sortByExpression As String, startRowIndex As Integer, maximumRows As Integer, ByRef totalRowCount As Integer) As IQueryable(Of Employee)
....
End Function
In the second signature the developer have to build query which sort and page the datasource items.
When we run the page, the data bound controls will call the above method and automatically retrieve the data and render it. The method has to return IEnumerable or IQueryable. Thus users could easily page and sort through the data within our bound controls. The benefits are that our controls will automatically add the appropriate sort and page operators onto an IQueryable query before executing it.
For example if SelectMethod returns data from Linq DataContext and if the paging of the bound control is turned on, the executed database query will return only items for the current page. If the bound control is sorted by a column the sorting also will be executed on the database and the sorted result will be returned. That is because the Linq will optimize the query to perform the sort and page operation as part of the database query.
The returned query needs to be sorted by using OrderBy when LinqToEntities is used, otherwise the exception: The method 'Skip' is only supported for sorted input in LINQ to Entities. The method 'OrderBy' must be called before the method 'Skip' will be thrown. MultiColumnsorting is NOT supported when the ModelBinding is used.
Hierarchical RadGrid is NOT supported. In order to use RadGrid hierarchy you need to use the Declarative Relations or Advanced Data Binding and programmatic hierarchy binding. RadGrid calls its SelectMethod twice (once for the grid and once for the MasterTableView) although SelectMethod for the MasterTableView is not declared.The select method must be called twice because the RadGrid calls its base.DataBind() and then the MasterTableVeiw calls its base.DataBind() method. So the framework calls SelectMethod twice, however only one database query is executed to get all data for building items in the MasterTableVeiw.
public IQueryable<Employee> GetProducts(string sortByExpression, int? startRowIndex, int? maximumRows, out int totalRowCount)
{
....
}
Public Function GetProducts(sortByExpression As String, startRowIndex As System.Nullable(Of Integer), maximumRows As System.Nullable(Of Integer), ByRef totalRowCount As Integer) As IQueryable(Of Employee)
....
End Function
Model Binding Filtering
In order to filter the data source of the data bound control and pass the filtered data to the control you could pass filter parameters to the SelectMethod. You could get these parameters from query string, cookies, form values, controls, viewstate, session and profile. For example:
public IQueryable<Product> GetProducts([Control("RadComboBoxCategories")] int? categoryID, [QueryString]string name)
{
// Filter the data source based on categoryID and ProductName
}
Public Function GetProducts(<Control("RadComboBoxCategories")> categoryID As System.Nullable(Of Integer), <QueryString> name As String) As IQueryable(Of Product)
' Filter the data source based on categoryID and ProductName
End Function
The code snippet above will get the name parameter from the QueryString and integer value of the selected item of the RadComboBox with ID equals to “RadComboBoxCategories”.
When the control is used to pass the filter parameter the control needs to perform post back and the Rebind() method of our data bound control need to be called in order to call the SelectMethod. Otherwise the SelectMethod will not be called and the new data source will not be passed to the data bound control. Need to add System.Web.ModelBinding namespace on the page
Model Binding CRUD operations
Editing
In order to have editing enabled into the data bound controls you need to set the UpdateMethod of the corresponding control to the web form page’s method. The UpdateMethod can have following signature:
public void UpdateProduct(int ProductID)
{
Product updatedProduct = context.Products.Where(p => p.ProductID == ProductID).First();
TryUpdateModel(updatedProduct);
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
Public Sub UpdateProduct(ProductID As Integer)
Dim updatedProduct As Product = context.Products.Where(Function(p) p.ProductID = ProductID).First()
TryUpdateModel(updatedProduct)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
Where the “ProductID” is one of the fields set as DataKeyNames of the corresponding bound control.
Or you could use following signature:
public void UpdateProduct(Product product)
{
Product updatedProduct = context.Products.Where(p => p.ProductID == product.ProductID).First();
TryUpdateModel(updatedProduct);
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
Public Sub UpdateProduct(product As Product)
Dim updatedProduct As Product = context.Products.Where(Function(p) p.ProductID = product.ProductID).First()
TryUpdateModel(updatedProduct)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
Inserting
In order to have inserting enabled into the data bound controls you need to set the InsertMethod property of the corresponding control to the name of the web form page’s insert method. The InsertMethod can have following signatures.
You can pass a Product object:
public void InsertProduct(Product p)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p);
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
Public Sub InsertProduct(p As Product)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p)
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
Or you can pass the productID to the Insert method.
public void InsertProduct(int productID)
{
Product pr = new Product();
TryUpdateModel(pr);
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p);
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
Public Sub InsertProduct(productID As Integer)
Dim pr As New Product()
TryUpdateModel(pr)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p)
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
Deleting
In order to have deleting enabled into the data bound controls you need to set the DeleteMethod property of the corresponding control to the name of the web form page’s delete method. The DeleteMethod can have following signature:
public void DeleteProduct(int ProductID)
{
Product deletedProduct = context.Products.Where(p => p.ProductID == ProductID).First();
context.Products.DeleteOnSubmit(deletedProduct);
context.SubmitChanges();
}
Public Sub DeleteProduct(ProductID As Integer)
Dim deletedProduct As Product = context.Products.Where(Function(p) p.ProductID = ProductID).First()
context.Products.DeleteOnSubmit(deletedProduct)
context.SubmitChanges()
End Sub
ModelBinding Validation
Due to the fact that Model Binding system in Web Forms supports model validation using the same validation attributes from the System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations you could use validation into our databound controls. You could decorate properties from your model classes with the attributes provided in System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations namespace. For example if you have DataContext mapped to a Northwind database “Product” table and you want to ensure that when inserting new product or update existing one the ProductName field is populated, you could set [Required] attribute to it into the DataClasses.designer.cs file:
[Required]
[global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage = "_ProductName", DbType = "NVarChar(40) NOT NULL", CanBeNull = false)]
public string ProductName
{
get
{
return this._ProductName;
}
set
{
if ((this._ProductName != value))
{
this.OnProductNameChanging(value);
this.SendPropertyChanging();
this._ProductName = value;
this.SendPropertyChanged("ProductName");
this.OnProductNameChanged();
}
}
}
<Required> _
<System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage := "_ProductName", DbType := "NVarChar(40) NOT NULL", CanBeNull := False)> _
Public Property ProductName() As String
Get
Return Me._ProductName
End Get
Set
If (Me._ProductName <> value) Then
Me.OnProductNameChanging(value)
Me.SendPropertyChanging()
Me._ProductName = value
Me.SendPropertyChanged("ProductName")
Me.OnProductNameChanged()
End If
End Set
End Property
Then when values from databound control editors are submitted to the server the the Web Forms Model Binding system will track whether any of these validation rules are violated in the page's ModelState property.
public void InsertProduct(Product p)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p);
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
Public Sub InsertProduct(p As Product)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p)
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
To show any validation errors you could use asp:ValidationSummary control or asp:ModelErrorMessage:
<asp:ValidationSummary runat="server" ID="ValidationSummary1" />
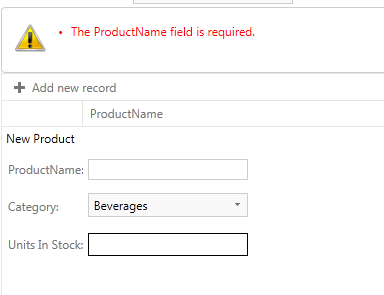
You need to call TryUpdateModel(object) before checking the ModelState.IsValid when inserting items. Otherwise the validation will not track any errors. The other approach is to pass the entire object as a parameter to the function:
public void InsertProduct(int productID)
{
Product pr = new Product();
TryUpdateModel(pr);
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p);
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
public void InsertProduct(Product p)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p);
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
Public Sub InsertProduct(productID As Integer)
Dim pr As New Product()
TryUpdateModel(pr)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p)
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
Public Sub InsertProduct(p As Product)
If ModelState.IsValid Then
context.Products.InsertOnSubmit(p)
context.SubmitChanges()
End If
End Sub
ModelBinding Limitations
We do not support model binding when the ViewState of the page is disabled. In order to use the model binding you need to set Page.EnableViewState = “true”