Getting Started with the DropDownTree
This tutorial explains how to set up a basic Telerik UI for ASP.NET MVC DropDownTree and highlights the major steps in the configuration of the component.
You will initialize a DropDownTree control and bind it to data. Next, you will handle some of the DropDownTree events.
After completing this guide, you will achieve the following result:
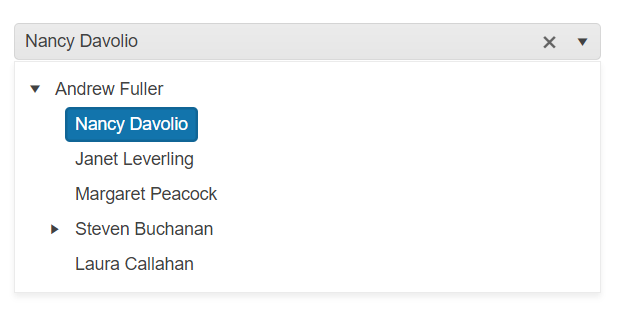
Prerequisites
To successfully complete the tutorial, you need a project that is already configured to use the Telerik UI for ASP.NET MVC components:
To create a new pre-configured project for the Telerik UI for ASP.NET MVC components, you can use a project template.
To manually configure an existing project by using NuGet, see the Adding Telerik UI through NuGet.
1. Prepare the CSHTML File
The first step is to add the required directives at the top of the .cshtml document:
-
To use the Telerik UI for ASP.NET MVC HtmlHelpers:
@using Kendo.Mvc.UI
Optionally, you can structure the document by adding the desired HTML elements like headings, divs, paragraphs, and others.
2. Declare the View Model
Declare the EmployeeViewModel view model.
The model must have a property field that represents the hierarchical relationship of the entries. In this tutorial, this is the
ReportsTofield.The
hasChildrenproperty of the model is required to render items as parent nodes on the client-side.
public class EmployeeViewModel
{
public int EmployeeID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int? ReportsTo { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public bool hasChildren { get; set; }
}
3. Initialize the DropDownTree
Use the DropDownTree HtmlHelper to add the component to a page and set some of its options.
- The
Name()configuration assigns a name to the instance of the helper—this is mandatory as its value is used for theidand thenameattributes of the DropDownTree element. - Configure the
DataTextFieldof the DropDownTree to bind the items of the popup to a field of theEmployeeViewModel. - Add the
DataSource()configuration option and set theReadend point.
@using Kendo.Mvc.UI
<label for="dropdowntree">Employees:</label>
@(Html.Kendo().DropDownTree()
.Name("dropdowntree")
.DataTextField("Name")
.DataSource(dataSource => dataSource
.Read(read => read
.Action("Get_Employees", "DropDownTree")
)
)
)
4. Declare the Read Action
In the Home controller, declare the Get_Employees action that you set to the DataSource Read configuration in the previous step.
public List<EmployeeViewModel> GetFlatData()
{
List<EmployeeViewModel> employees = new List<EmployeeViewModel>(){
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 1,
Name = "Nancy Davolio",
Title = "Sales Representative",
ReportsTo = 2,
hasChildren = false
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 2,
Name = "Andrew Fuller",
Title = "Vice President, Sales",
ReportsTo = null,
hasChildren = true
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 3,
Name = "Janet Leverling",
Title = "Sales Representative",
ReportsTo = 2,
hasChildren = false
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 4,
Name = "Margaret Peacock",
Title = "Sales Representative",
ReportsTo = 2,
hasChildren = false
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 5,
Name = "Steven Buchanan",
Title = "Sales Manager",
ReportsTo = 2,
hasChildren = true
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 6,
Name = "Michael Suyama",
Title = "Sales Representative",
ReportsTo = 5,
hasChildren = false
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 7,
Name = "Robert King",
Title = "Sales Representative",
ReportsTo = 5,
hasChildren = false
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 8,
Name = "Laura Callahan",
Title = "Inside Sales Coordinator",
ReportsTo = 2,
hasChildren = false
},
new EmployeeViewModel {
EmployeeID = 9,
Name = "Anne Dodsworth",
Title = "Sales Representative",
ReportsTo = 5,
hasChildren = false
}
}
return employees;
}
public JsonResult Get_Employees([DataSourceRequest] DataSourceRequest request, int? id)
{
var data = GetFlatData();
var result = from e in data.Employees
where (id.HasValue ? e.ReportsTo == id : e.ReportsTo == null)
select new
{
id = e.EmployeeID,
Name = e.FirstName + " " + e.LastName,
hasChildren = (from q in data.Employees
where (q.ReportsTo == e.EmployeeID)
select q
).Count() > 0
};
return Json(result.ToTreeDataSourceResult(request));
}
5. Handle the DropDownTree Events
The DropDownTree exposes various events that you can handle and further customize the functionality of the component. In this tutorial, you will use the DataBound event of the DropDownTree.
@using Kendo.Mvc.UI
<label for="dropdowntree">Employees:</label>
@(Html.Kendo().DropDownTree()
.Name("dropdowntree")
.DataTextField("Name")
.DataSource(dataSource => dataSource
.Read(read => read
.Action("Get_Employees", "DropDownTree")
)
)
.Events(e=>e.DataBound("onDataBound"))
)
<script>
function onDataBound(e) {
console.log("DropDownTree data bound");
}
</script>
For more examples, refer to the demo on using the events of the DropDownTree.
6. (Optional) Reference Existing DropDownTree Instances
To use the client-side API of the DropDownTree and build on top of its initial configuration, you need a reference to the DropDownTree instance. Once you get a valid reference, you can call the respective API methods:
-
Use the
.Name()(idattribute) of the component instance to get a reference.<script> var dropdowntreeReference = $("#dropdowntree").data("kendoDropDownTree"); // dropdowntreeReference is a reference to the existing instance of the helper. </script> -
Use the DropDownTree client-side API to control the behavior of the widget. In this example, you will use the
openmethod to open the popup of the DropDownTree programmatically.<script> $(document).ready(function () { var dropdowntreeReference = $("#dropdowntree").data("kendoDropDownTree"); dropdowntreeReference.open(); }) </script>
For more information on referencing specific helper instances, see the Methods and Events article.