Exporting Data from DataGridView Control to Excel File
Environment
| Version | Product | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 2025.4.1104 | RadSpreadProcessing | Desislava Yordanova |
Description
Export the data from a WinForms DataGridView control to an Excel file in XLSX format, including header information. I want to achieve this using Telerik Document Processing RadSpreadProcessing in a Visual Studio C# Windows Forms application.
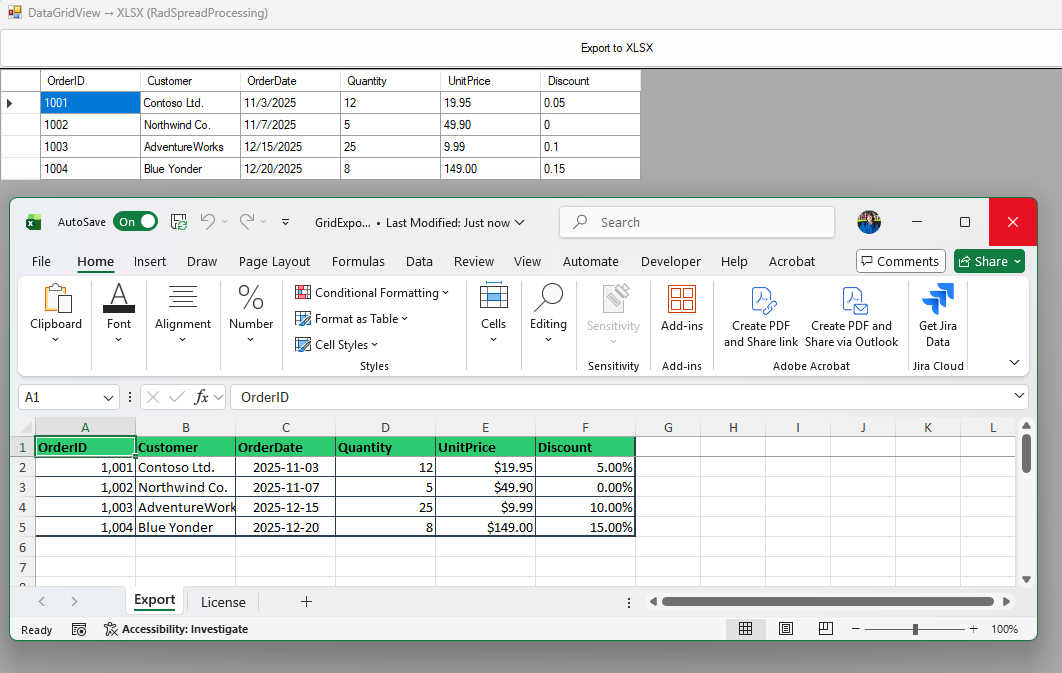
Solution
Use Telerik Document Processing RadSpreadProcessing to create an Excel file programmatically. Follow these steps:
- Create a Windows Forms application and add a DataGridView control to display your data.
- Add a button to trigger the export functionality.
- Use RadSpreadProcessing to export data from the DataGridView to an Excel file.
Here is the complete example:
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private DataGridView _grid;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button _btnExport;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.Text = "DataGridView → XLSX (RadSpreadProcessing)";
this.Width = 900;
this.Height = 500;
_grid = new DataGridView
{
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
AutoGenerateColumns = true,
AllowUserToAddRows = false,
ReadOnly = true
};
_btnExport = new System.Windows.Forms.Button
{
Text = "Export to XLSX",
Dock = DockStyle.Top,
Height = 40
};
_btnExport.Click += OnExportClick;
this.Controls.Add(_grid);
this.Controls.Add(_btnExport);
LoadSampleData();
}
private void LoadSampleData()
{
// Create a simple DataTable with mixed types
var table = new DataTable("Orders");
table.Columns.Add("OrderID", typeof(int));
table.Columns.Add("Customer", typeof(string));
table.Columns.Add("OrderDate", typeof(DateTime));
table.Columns.Add("Quantity", typeof(int));
table.Columns.Add("UnitPrice", typeof(decimal));
table.Columns.Add("Discount", typeof(double)); // as percent (0.0 .. 1.0)
// Sample rows
table.Rows.Add(1001, "Contoso Ltd.", new DateTime(2025, 11, 3), 12, 19.95m, 0.05);
table.Rows.Add(1002, "Northwind Co.", new DateTime(2025, 11, 7), 5, 49.90m, 0.00);
table.Rows.Add(1003, "AdventureWorks", new DateTime(2025, 12, 15), 25, 9.99m, 0.10);
table.Rows.Add(1004, "Blue Yonder", new DateTime(2025, 12, 20), 8, 149.00m, 0.15);
_grid.DataSource = table;
}
private void OnExportClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_grid.DataSource == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("No data to export.");
return;
}
using (var sfd = new SaveFileDialog
{
Filter = "Excel Workbook (*.xlsx)|*.xlsx",
FileName = "GridExport.xlsx",
Title = "Save XLSX"
})
{
if (sfd.ShowDialog(this) != DialogResult.OK)
return;
try
{
ExportGridToXlsx(sfd.FileName);
if (MessageBox.Show("Export complete. Open file?", "Export", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Information) == DialogResult.Yes)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(new System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo
{
FileName = sfd.FileName,
UseShellExecute = true
});
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"Export failed:\n{ex.Message}", "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
private void ExportGridToXlsx(string filePath)
{
// Build a workbook in memory
var workbook = new Workbook();
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add();
worksheet.Name = "Export";
// Optional: page setup and margins if you later print or export to PDF
var ps = worksheet.WorksheetPageSetup;
ps.PageOrientation = PageOrientation.Portrait;
ps.PaperType = PaperTypes.A4;
ps.Margins = new PageMargins(20, 20, 20, 20); // points
// Write headers (DataGridView columns)
int colCount = _grid.Columns.Count;
int rowCount = _grid.Rows.Count;
// Set some column widths and write header text bold
for (int c = 0; c < colCount; c++)
{
var headerText = _grid.Columns[c].HeaderText;
var headerCell = worksheet.Cells[0, c];
headerCell.SetValue(headerText);
// Bold & fill color for header:
var headerSel = worksheet.Cells[0, c];
headerSel.SetIsBold(true);
PatternFill solidPatternFill = new PatternFill(PatternType.Solid, System.Windows.Media.Color.FromArgb(255, 46, 204, 113), Colors.Transparent);
headerSel.SetFill(solidPatternFill);
headerSel.SetVerticalAlignment(RadVerticalAlignment.Center);
// Auto width guess: you can adjust per your needs
worksheet.Columns[c].SetWidth(new ColumnWidth(100, true)); // 100 pixels approx.
}
// Write data rows
for (int r = 0; r < rowCount; r++)
{
var gridRow = _grid.Rows[r];
for (int c = 0; c < colCount; c++)
{
var cell = worksheet.Cells[r + 1, c]; // +1 because row 0 is header
object value = gridRow.Cells[c].Value;
// Set value by type for proper Excel typing & formatting later
if (value is null || value == DBNull.Value)
{
cell.SetValue(string.Empty);
continue;
}
var type = value.GetType();
if (type == typeof(int))
{
cell.SetValue(Convert.ToInt32(value));
// Example: integer with thousands sep → "#,##0"
cell.SetFormat(new CellValueFormat("#,##0"));
cell.SetHorizontalAlignment(RadHorizontalAlignment.Right);
}
else if (type == typeof(decimal) || type == typeof(double) || type == typeof(float))
{
double d = Convert.ToDouble(value, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
// Detect if the column name looks like price/amount to apply currency-ish format,
// or if Discount/Percent → percentage format. Customize as needed:
string header = _grid.Columns[c].HeaderText?.ToLowerInvariant() ?? string.Empty;
if (header.Contains("price") || header.Contains("amount") || header.Contains("unit"))
{
cell.SetValue(d);
cell.SetFormat(new CellValueFormat("$#,##0.00")); // set currency symbol or use custom
}
else if (header.Contains("discount") || header.Contains("percent"))
{
cell.SetValue(d); // e.g., 0.15
cell.SetFormat(new CellValueFormat("0.00%")); // renders as 15.00%
}
else
{
cell.SetValue(d);
cell.SetFormat(new CellValueFormat("#,##0.00"));
}
cell.SetHorizontalAlignment(RadHorizontalAlignment.Right);
}
else if (type == typeof(DateTime))
{
cell.SetValue((DateTime)value);
// Excel-style date format (adjust to your locale)
cell.SetFormat(new CellValueFormat("yyyy-mm-dd")); // ISO-like
cell.SetHorizontalAlignment(RadHorizontalAlignment.Center);
}
else
{
// Treat as text
cell.SetValue(Convert.ToString(value, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
}
}
// Add table borders (optional): apply thin border to used range
var used = worksheet.UsedCellRange;
if (used != null)
{
ThemableColor darkBlue = new ThemableColor(System.Windows.Media.Color.FromArgb(255, 44, 62, 80));
CellBorders darkBlueBorders = new CellBorders(
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Medium, darkBlue), // Left border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Medium, darkBlue), // Top border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Medium, darkBlue), // Right border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Medium, darkBlue), // Bottom border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Thin, darkBlue), // Inside horizontal border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Thin, darkBlue), // Inside vertical border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.None, darkBlue), // Diagonal up border
new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.None, darkBlue)); // Diagonal down border
worksheet.Cells[used.FromIndex.RowIndex, used.FromIndex.ColumnIndex, used.ToIndex.RowIndex, used.ToIndex.ColumnIndex]
.SetBorders(darkBlueBorders);
}
// Optional: freeze header row
worksheet.ViewState.FreezePanes(1, 0);
// Save to XLSX
var xlsx = new XlsxFormatProvider();
using (var fs = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write))
{
xlsx.Export(workbook, fs, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10));
}
}
}