Preventing Excel From Extending Cell Formatting Below Formatted Range Using SpreadProcessing
Environment
| Version | Product | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 2025.2.520 | RadSpreadProcessing | Desislava Yordanova |
Description
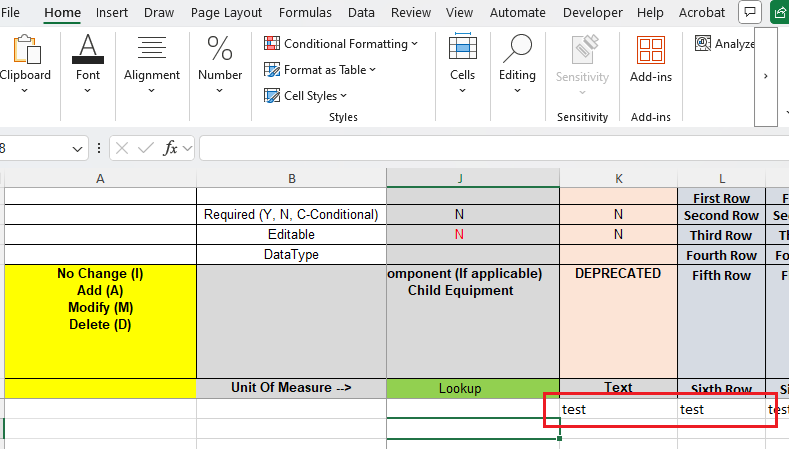
When exporting an Excel file using SpreadProcessing and applying formatting to a range of cells, entering data immediately below the formatted range may cause Excel to automatically extend the formatting:
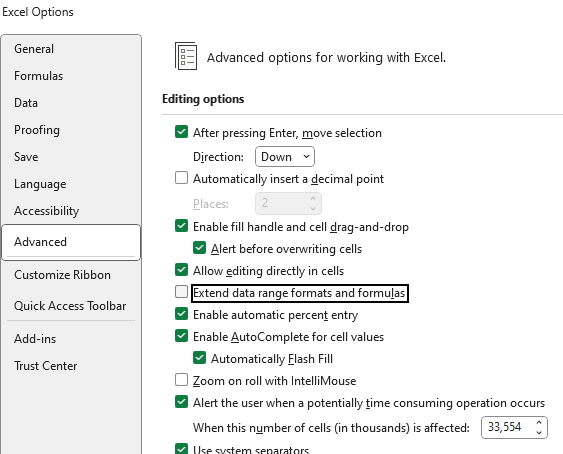
Extend Data Range Formats and Formulas
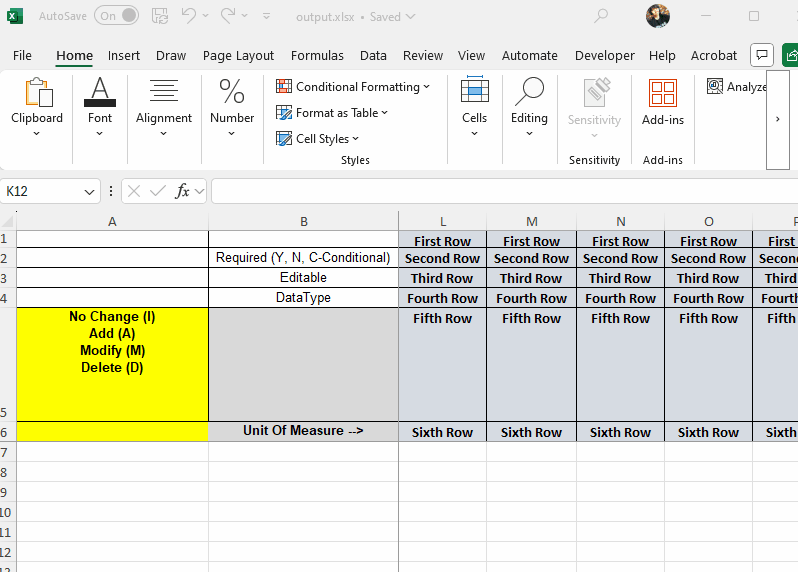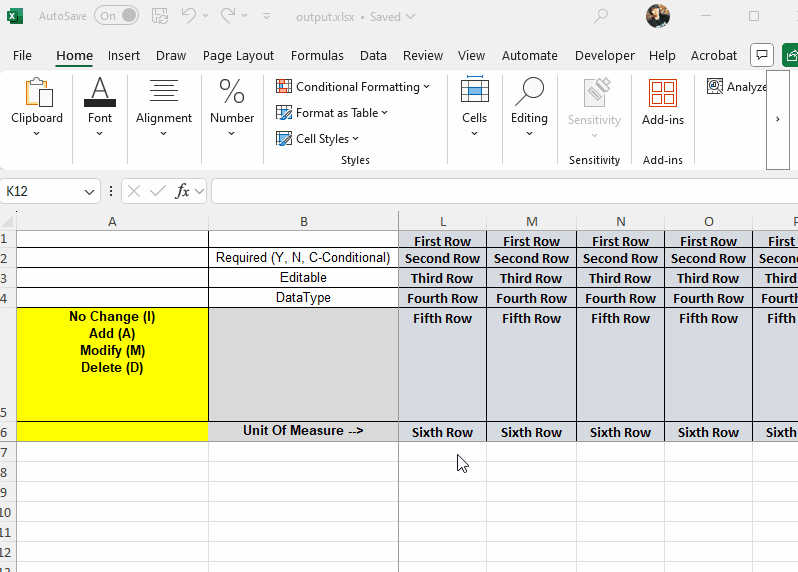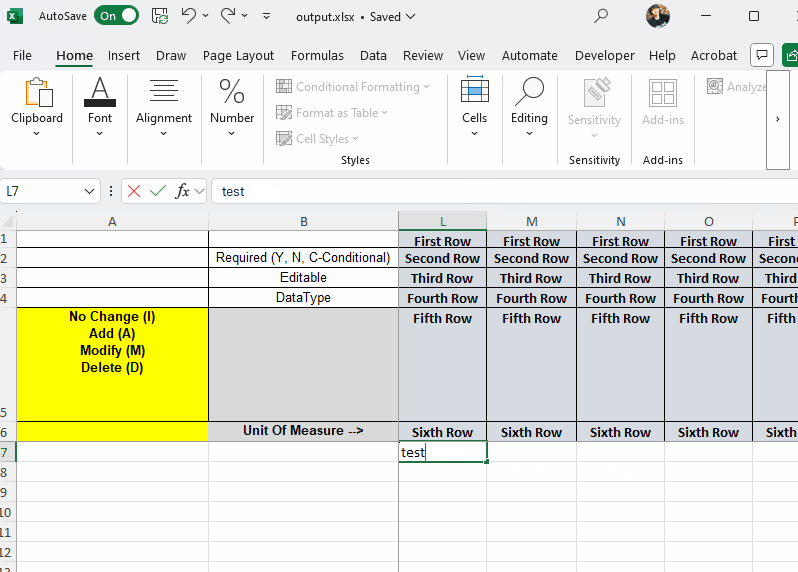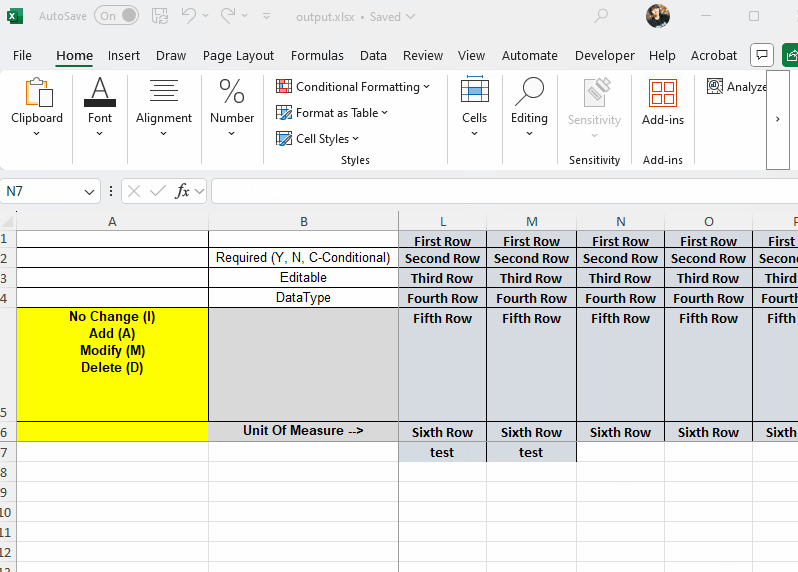
This occurs due to Excel's built-in "Extend data range formats and formulas" feature. The behavior is controlled by Excel itself and cannot be disabled programmatically from within the SpreadProcessing library:
Clearing the formatting of cells in a range below the formatted data helps mitigate behavior. However, this approach works only for pre-defined ranges and does not override Excel's internal settings permanently. This article demonstrates a sample approach how to rectify such a behavior.
Solution
To prevent Excel's automatic formatting extension, clear the formatting of cells in a specified range below the formatted and populated range. Use the following steps and code:
- Identify the used cell range in the worksheet.
- Define a range below the used cells that you want to clear formatting from.
- Apply default formatting (e.g., transparent fill, no borders, default alignment, etc.) to the defined range.
Use the following code example:
// Identify the used range in the worksheet
CellRange usedCellRange = worksheet.UsedCellRange;
int rowIndexStart = usedCellRange.ToIndex.RowIndex + 1;
int columnIndexStart = usedCellRange.FromIndex.ColumnIndex + 1;
int rowIndexEnd = rowIndexStart + 10; // Adjust the range size as needed
int columnIndexEnd = usedCellRange.ToIndex.ColumnIndex;
// Define the range to clear formatting
CellRange clearRange = new CellRange(rowIndexStart, columnIndexStart, rowIndexEnd, columnIndexEnd);
// Set transparent fill and default formatting
var clearColor = Colors.Transparent;
SetDefaultFormattingCellRange(worksheet, clearRange, clearColor);
// Helper method to apply default formatting
static void SetDefaultFormattingCellRange(Worksheet worksheet, CellRange cellRange, Color cellColor)
{
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetFill(new PatternFill(PatternType.Solid, cellColor, Colors.Transparent));
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetIsBold(false);
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetHorizontalAlignment(RadHorizontalAlignment.Left);
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetVerticalAlignment(RadVerticalAlignment.Center);
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetIsWrapped(false);
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetValue(string.Empty);
CellBorder border = new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.Thin, ThemableColor.FromColor(Colors.LightGray));
CellBorder noBorder = new CellBorder(CellBorderStyle.None, ThemableColor.FromColor(Colors.Black));
worksheet.Cells[cellRange].SetBorders(new CellBorders(
left: border,
top: border,
right: border,
bottom: border,
diagonalUp: noBorder,
diagonalDown: noBorder,
insideHorizontal: border,
insideVertical: border)
);
}
This approach minimizes the chances of Excel automatically extending formatting when new data is entered below the formatted range.