Traversing Documents with Empty Cells When Reading Excel Rows Using RadSpreadStreamProcessing
Environment
| Version | Product | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 2025.4.1104 | RadSpreadProcessing | Desislava Yordanova |
Description
While using RadSpreadStreamProcessing to read an Excel file, unexpected results may occur when reading rows that contain empty cells. Empty cells are skipped, causing misalignment of data with columns. For example, when a row has blank values in the first columns, the value of the subsequent column with data shifts to the wrong column index.
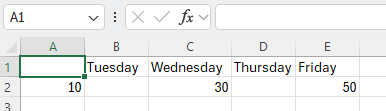
This may lead to unexpected difficulties if you need to traverse the data rows stored in the Excel document and populate a DataTable.
This knowledge base article also answers the following questions:
- How to read Excel rows with empty cells using RadSpreadStreamProcessing?
- How to maintain column alignment when reading Excel rows with empty cells?
- How to insert DBNull.Value for empty cells in imported Excel rows?
Solution
To ensure empty cells are correctly handled and data aligns with the columns, adjust the reading logic to account for skipped cells. Use the following code snippet:
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
string fileName = "Book1.xlsx";
using (System.IO.FileStream fs = new System.IO.FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Open))
{
using (IWorkbookImporter workBookImporter = SpreadImporter.CreateWorkbookImporter(SpreadDocumentFormat.Xlsx, fs))
{
foreach (IWorksheetImporter worksheetImporter in workBookImporter.WorksheetImporters)
{
foreach (IRowImporter rowImporter in worksheetImporter.Rows)
{
// Define columns based on the first row
if (rowImporter.RowIndex == 0)
{
var cellIndex = 0;
foreach (ICellImporter cell in rowImporter.Cells)
{
while (cellIndex < cell.ColumnIndex)
{
dt.Columns.Add("Column_" + cellIndex);
cellIndex++;
}
dt.Columns.Add(cell.Value?.ToString() ?? "Column_" + cellIndex);
cellIndex++;
}
}
else
{
var newRow = dt.NewRow();
var cellIndex = 0;
foreach (ICellImporter cell in rowImporter.Cells)
{
while (cellIndex < cell.ColumnIndex)
{
newRow[cellIndex] = DBNull.Value;
cellIndex++;
}
newRow[cellIndex] = cell.Value;
cellIndex++;
}
dt.Rows.Add(newRow);
}
}
}
}
}
Explanation
-
Define Columns: During iteration of the first row (header row), add columns to the
DataTable. If columns are skipped, add placeholder columns named "Column_X". -
Insert DBNull.Value for Empty Cells: For subsequent rows, check for skips in cell indices. Insert
DBNull.Valuefor every skipped cell index before adding the next non-empty cell value. -
Add Rows: Append the constructed row to the
DataTable.
This logic ensures that all cells, including empty ones, are accounted for, maintaining alignment with the Excel file's structure.