How to Access a SQL Database in Code
You can access an SQL database in a data driven test, as seen here. This is built-in functionality for Test Studio, but not for Telerik Testing Framework. This article demonstrates how to access a SQL database through code, which allows for greater flexibility. Also, writing into a database is only possible with a coded solution.
Add Assembly Reference
Use the System.Data.SqlClient API. You'll need to add an assembly reference to it, as seen here. This API is part of the System.Data assembly. This assembly is located, by default, in the following location (on a 64-bit Windows 7 machine with .NET 4.0):
C:\Program Files (x86)\Reference Assemblies\Microsoft\Framework.NETFramework\v4.0\Profile\Client\System.Data.dll
If a reference to System.Data 2.0 already exists, remove it add it again from the above directory for the 4.0 version.
Ensure you add the using or Imports statement to the top of the code-behind file. Click the View Class button, scroll to the top of the code, and add this line:
using System.Data.SqlClient;
Imports System.Data.SqlClient;
Sample Code
Here we've create a SQL database named myFirstDB. This database contains a table named Table_1. This table contains a column named City.
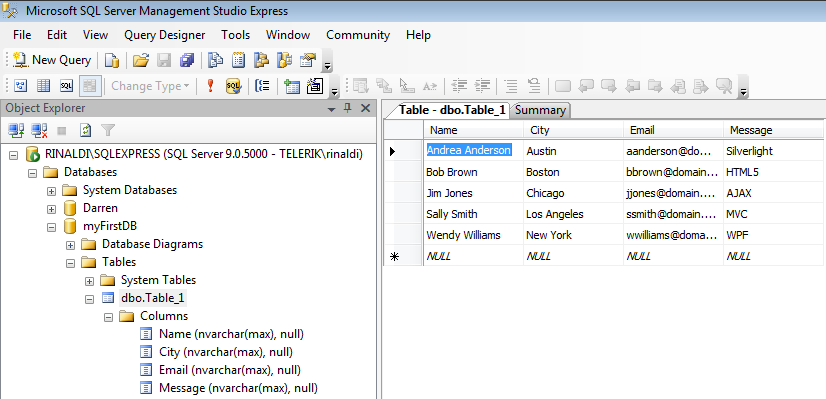
Read from SQL Database
//Define a new SQL connection with a connection string.
//The connection string will be different depending on your environment and the name of the database, table, etc.
//See http://www.connectionstrings.com for connection string examples.
SqlConnection thisConnection = new SqlConnection("Data Source=MACHINENAME\\SQLEXPRESS; Initial Catalog=myFirstDB; Integrated Security=true;");
thisConnection.Open();
//Write the name of the database to the log
Log.WriteLine(thisConnection.Database);
//Create an SQL command
SqlCommand thisCommand = thisConnection.CreateCommand();
//This is a simple SQL command that will go through all the values in the "City" column from the table "Table_1"
thisCommand.CommandText = "SELECT City FROM Table_1";
SqlDataReader thisReader = thisCommand.ExecuteReader();
while (thisReader.Read())
{
Log.WriteLine("Value of City column: " + (String) thisReader["City"]);
}
thisReader.Close();
thisConnection.Close();
'Define a new SQL connection with a connection string.
'The connection string will be different depending on your environment and the name of the database, table, etc.
'See http://www.connectionstrings.com for connection string examples.
Dim thisConnection As New SqlConnection("Data Source=MACHINENAME\SQLEXPRESS; Initial Catalog=myFirstDB; Integrated Security=true;")
thisConnection.Open()
'Write the name of the database to the log
Log.WriteLine(thisConnection.Database)
'Create an SQL command
Dim thisCommand As SqlCommand = thisConnection.CreateCommand()
'This is a simple SQL command that will go through all the values in the "City" column from the table "Table_1"
thisCommand.CommandText = "SELECT City FROM Table_1"
Dim thisReader As SqlDataReader = thisCommand.ExecuteReader()
While thisReader.Read()
Log.WriteLine("Value of City column: " + DirectCast(thisReader("City"), [String]))
End While
thisReader.Close()
thisConnection.Close()
Write into SQL Database
//Define a new SQL connection with a connection string.
//The connection string will be different depending on your environment and the name of the database, table, etc.
//See http://www.connectionstrings.com for connection string examples.
SqlConnection thisConnection = new SqlConnection("Data Source=MACHINENAME\\SQLEXPRESS; Initial Catalog=myFirstDB; Integrated Security=true;");
thisConnection.Open();
//Write the name of the database to the log.
Log.WriteLine(thisConnection.Database);
//Create a SQL command to insert a new value into the "City" column.
SqlCommand thisCommand = thisConnection.CreateCommand();
thisCommand.CommandText = "INSERT INTO Table_1 (City) VALUES ('Richmond')";
thisCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
'Define a new SQL connection with a connection string.
'The connection string will be different depending on your environment and the name of the database, table, etc.
'See http://www.connectionstrings.com for connection string examples.
Dim thisConnection As New SqlConnection("Data Source=MACHINENAME\SQLEXPRESS; Initial Catalog=myFirstDB; Integrated Security=true;")
thisConnection.Open()
'Write the name of the database to the log.
Log.WriteLine(thisConnection.Database)
'Create a SQL command to insert a new value into the "City" column.
Dim thisCommand As SqlCommand = thisConnection.CreateCommand()
thisCommand.CommandText = "INSERT INTO Table_1 (City) VALUES ('Richmond')"
thisCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
Note: This code won't run without modification. The database, table, and column in the original code won't exist in your environment.