Timeline View
Timeline View
Introduction
The Fiddler Classic Timeline View allows you to visualize the HTTP(S) traffic on a "waterfall" diagram.
Hovering over any entry will show more information about the entry. Double-clicking the entry will inspect that session.
How is the diagram interpreted
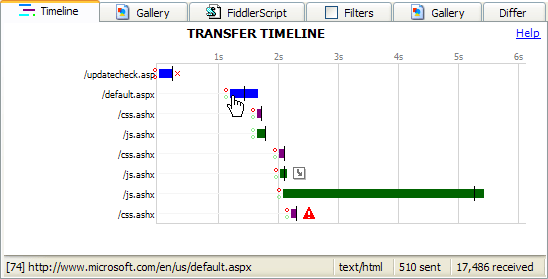
The abbreviated URL at the left of each Transfer Bar is green if the request was a Conditional Request, or Black if the request was unconditional. The full URL is shown in the status bar on hover.
The start of the transfer bar is drawn at the time (Timers.ClientBeginRequest) when the client sends the request to Fiddler.
The end of the transfer bar is drawn at the time (Timers.ClientDoneResponse) when the response to the client is completed.
The color of the bar is determined by the MIME type of the response; light-green for images, dark-green for JavaScript, purple for CSS, and blue otherwise.
If the bar is "hatched" rather than smooth, this indicates that the HTTP response was buffered by Fiddler. For more information, see the "What is streaming?" section below.
The vertical line indicates the time to first byte of the server's response (Timers.ServerBeginResponse).
The green circle before the bar shows that a connection was reused; a red circle means that the connection was newly created.
The top circle represents the client's connection to Fiddler; the bottom circle represents Fiddler's connection to the server.
A red X after the bar indicates that the server sent a Connection: close header (or failed to send a Keep-Alive header for a HTTP/1.0 response), preventing subsequent reuse of the connection.
The gray arrow icon indicates that the server's response was a redirect (302). The red ! icon indicates that the server returned an error code (4xx, 5xx).
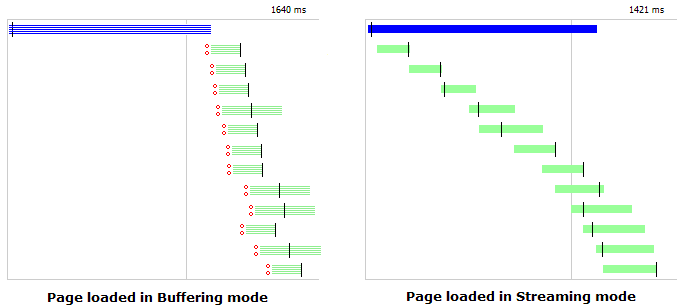
What is streaming mode?
Streaming mode ensures that HTTP responses are not buffered by Fiddler. Buffering alters the waterfall diagram, as you can see below, where none of the images begin to download until their containing page completes. Learn more...