Use Fiddler Classic as a Reverse Proxy
Configure Fiddler Classic as Reverse Proxy
To use this method, the hostname for the request to reroute must be 127.0.0.1:8888, localhost:8888, [::1]:8888, or the machine's NETBIOS hostname on port 8888.
-
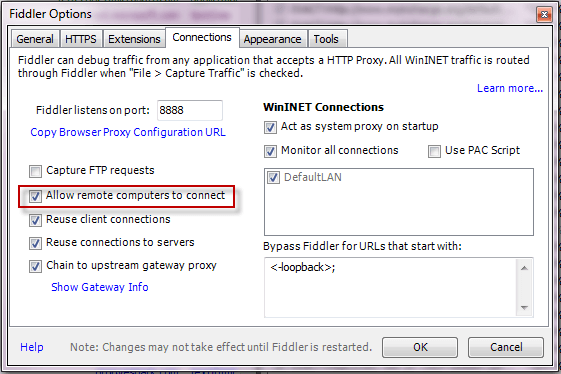
Click Tools > Options. Ensure Allow remote clients to connect is checked.
Close Fiddler Classic.
Start REGEDIT.
Create a new DWORD named ReverseProxyForPort inside HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Fiddler2.
Set the DWORD to the local port where Fiddler Classic will re-route inbound traffic (usually port 80 for a standard HTTP server).
Restart Fiddler Classic.
In a browser, go to http://127.0.0.1:8888.
Write a FiddlerScript Rule
-
Click Tools > Options. Ensure Allow remote clients to connect is checked.

Click Tools > Options, and ensure the "Allow remote clients to connect" checkbox is checked.
Restart Fiddler Classic if prompted.
Click Rules > Customize Rules.
-
Inside the OnBeforeRequest handler*, add a new line of code:
if (oSession.host.toLowerCase() == "webserver:8888") oSession.host = "webserver:80"; Using a browser on the client machine, go to http://webserver:8888.
Configure Fiddler Classic to Listen to Client Application Target Port
Reconfigure your target server to listen on a different port. For example, if a web server runs on port 80, reconfigure it to run on port 81.
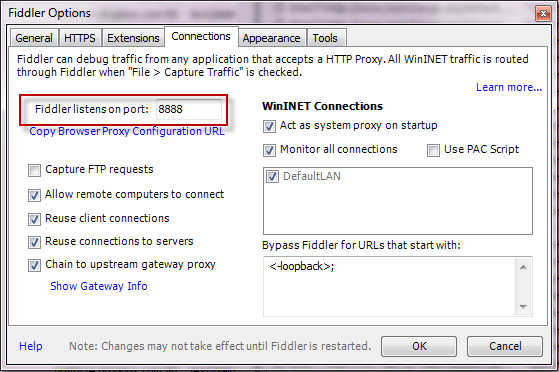
Click Tools > Options....
Click Connections.
-
Type the client's target port number next to Fiddler listens to port:
Configure Fiddler Classic as a reverse proxy or write a FiddlerScript Rule to re-route traffic to the target server's new port (described above).