Horizontal Inheritance
This tutorial teaches you how to create horizontal inheritance mapping by using the Fluent Mapping API. Horizontal inheritance can only be enabled for the topmost class in a hierarchy. Each immediate subclass is stored in its own table with a "copy" of the fields from the superclass. A horizontally mapped class itself, i.e. the superclass, does not have a table. Therefore, a horizontally mapped class cannot be directly persisted; only subclasses of the class can be stored in the database. For this reason, it is recommended (but not required) for horizontally mapped classes to be declared as abstract.
Modeling Horizontal Inheritance
The following example demonstrates how to model horizontal inheritance for the Animal hierarchy. You need to set the inheritance strategy by using the Inheritance method only for the base (root) class. Another specific moment is that you have to specify primary keys only for the derived classes in the hierarchy, e.g. Cat and Dog.
public class FluentModelMetadataSource : FluentMetadataSource
{
protected override IList<MappingConfiguration> PrepareMapping()
{
List<MappingConfiguration> configurations = new List<MappingConfiguration>();
MappingConfiguration<Animal> animalConfiguration = new MappingConfiguration<Animal>();
animalConfiguration.MapType().Inheritance( Telerik.OpenAccess.InheritanceStrategy.Horizontal );
MappingConfiguration<Dog> dogConfiguration = new MappingConfiguration<Dog>();
dogConfiguration
.MapType(x => new
{
BestFriend = x.BestFriend,
DogId = x.Id,
DogName = x.Name
}).ToTable("Dog");
dogConfiguration.HasProperty(d => d.Id).IsIdentity(KeyGenerator.Autoinc);
MappingConfiguration<Cat> catConfiguration = new MappingConfiguration<Cat>();
catConfiguration.MapType(x => new
{
LivesLeft = x.LivesLeft,
CatId = x.Id
}).ToTable("Cat");
catConfiguration.HasProperty( d => d.Id ).IsIdentity( KeyGenerator.Autoinc );
configurations.Add( animalConfiguration );
configurations.Add( catConfiguration );
configurations.Add( dogConfiguration );
return configurations;
}
}
Public Class FluentModelMetadataSource
Inherits FluentMetadataSource
Protected Overrides Function PrepareMapping() As _
System.Collections.Generic.IList(Of Telerik.OpenAccess.Metadata.Fluent.MappingConfiguration)
Dim configurations As List(Of MappingConfiguration) = New List(Of MappingConfiguration)()
Dim animalConfiguration As New MappingConfiguration(Of Animal)()
animalConfiguration.MapType().Inheritance(Telerik.OpenAccess.InheritanceStrategy.Horizontal)
animalConfiguration.FieldNamingRules.AddPrefix = "_"
Dim dogConfiguration As New MappingConfiguration(Of Dog)()
dogConfiguration.MapType(Function(x) New With {Key .BestFriend = x.BestFriend, Key .DogId = x.Id, Key .DogName = x.Name})
dogConfiguration.FieldNamingRules.AddPrefix = "_"
dogConfiguration.HasProperty(Function(x) x.Id).IsIdentity(KeyGenerator.Autoinc)
Dim catConfiguration As New MappingConfiguration(Of Cat)()
catConfiguration.MapType(Function(x) New With {Key .LivesLeft = x.LivesLeft, Key .CatId = x.Id})
catConfiguration.FieldNamingRules.AddPrefix = "_"
catConfiguration.HasProperty(Function(x) x.Id).IsIdentity(KeyGenerator.Autoinc)
configurations.Add(animalConfiguration)
configurations.Add(catConfiguration)
configurations.Add(dogConfiguration)
Return configurations
End Function
End Class
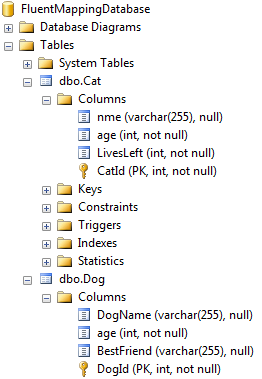
When you update your database schema to the latest model state, two tables will be created - Cat and Dog. Each subclass is stored in its own table with a "copy" of the fields from the base class.
Animal Class
public class Animal
{
public string Name {get;set;}
public int Age { get; set; }
}
Public Class Animal
Private _name As String
Public Property Name() As String
Get
Return _name
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
_name = value
End Set
End Property
Private _age As Integer
Public Property Age As Integer
Get
Return _age
End Get
Set(value As Integer)
_age = value
End Set
End Property
End Class
Cat Class
public class Cat : Animal
{
public int Id {get;set;}
public int LivesLeft {get;set;}
}
Public Class Cat
Inherits Animal
Private _id As Integer
Public Property Id() As Integer
Get
Return _id
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
_id = value
End Set
End Property
Private _livesLeft As Integer
Public Property LivesLeft() As Integer
Get
Return _livesLeft
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
_livesLeft = value
End Set
End Property
End Class
Dog Class
public class Dog : Animal
{
public int Id {get;set;}
public string BestFriend {get;set;}
}
Public Class Dog
Inherits Animal
Private _id As Integer
Public Property Id() As Integer
Get
Return _id
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
_id = value
End Set
End Property
Private _bestFriend As Integer
Public Property BestFriend() As Integer
Get
Return _bestFriend
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
_bestFriend = value
End Set
End Property
End Class