Virtualization Strategies
RadDataBoundListBox allows for using different Virtualization Strategies for its visual items. A Virtualization Strategy is basically the way visual items are created, ordered on the viewport and reused. There are three types of Virtualization Strategies that are shipped out-of-the-box:
- Stack Virtualization Strategy
- Wrap Virtualization Strategy
- Dynamic Grid Virtualization Strategy
Each of these virtualization strategies has its own properties that specify its behavior. Setting a virtualization strategy is performed by initializing a corresponding Virtualization Strategy Definition, setting its properties and assigning it to the VirtualizationStrategyDefinition property of RadDataBoundListBox.
By default, RadDataBoundListBox uses Stack Virtualization Strategy with its Orientation property set to Vertical.
Using Stack Virtualization Strategy in RadDataBoundListBox
To use Stack Virtualization Strategy in RadDataBoundListBox you have to set the VirtualizationStrategyDefinition property to an instance of the StackVirtualizationStrategyDefinition class.
The following XAML code snippet demonstrates how this is done:
<telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox x:Name="stackDataBoundListBox">
<telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox.VirtualizationStrategyDefinition>
<telerikDataControls:StackVirtualizationStrategyDefinition Orientation="Vertical"/>
</telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox.VirtualizationStrategyDefinition>
</telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox>
A StackVirtualizationStrategy manages the viewport by ordering the visual items in a stack layout. Items at the top and bottom edges of the stack are recycled to be further reused depending on the direction of scrolling.
To enable horizontal scrolling in RadDataBoundListBox you simply need to set the Orientation of the StackVirtualizationStrategyDefinition to Horizontal.
Using the ReorderMode property
The StackVirtualizationStrategyDefinition class exposes the ReorderMode property that accepts values from the CollectionChangeItemReorderMode enumeration. This property can be used to define how viewport items are repositioned when a collection change occurs in the source collection which implies updating the items in the viewport. The possible values are as follows:
- MoveItemsDown: this is the default option. Items below the changed item are repositioned.
- MoveItemsUp: Items above the changed item are repositioned.
Using Wrap Virtualization Strategy in RadDataBoundListBox
To use Wrap Virtualization Strategy in RadDataBoundListBox you have to set the VirtualizationStrategyDefinition property to an instance of the WrapVirtualizationStrategyDefinition class.
The following XAML code snippet demonstrates how this is done:
<telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox x:Name="wrapDataBoundListBox">
<telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox.VirtualizationStrategyDefinition>
<telerikDataControls:WrapVirtualizationStrategyDefinition Orientation="Vertical" WrapLineAlignment="Center"/>
</telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox.VirtualizationStrategyDefinition>
</telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox>
A WrapVirtualizationStrategy manages the viewport by ordering the visual items in a wrap layout. Just as the stack layout, a wrap layout supports two orientations: hirozontal and vertical. In horizontal mode, the wrap layout strategy orders the items in rows and scrolls them vertically, whereas in vertical mode - items are ordered in columns and scrolled horizontally.
Defining Orientation
You can define which wrap layout mode will be used by setting the Orientation property of the WrapVirtualizationStrategyDefinition instance.
Defining Wrap Line Alignment
You can define the alignment if the visual containers within a single Wrap Line by setting the WrapLineAlignment property exposed by WrapVirtualizationStrategyDefinition. This property accepts values from the WrapLineAlignment enumeration. Possible choices are:
- Near: this is the default value. Items are positioned starting at the beginning of the wrap line.
- Center: items are centered in the wrap line.
- End: items are positioned starting at the far end of the wrap line.
Using Dynamic Grid Virtualization Strategy in RadDataBoundListBox
To use Dynamic Grid Wrap Virtualization Strategy in RadDataBoundListBox you have to set the VirtualizationStrategyDefinition property to an instance of the DynamicGridVirtualizationStrategyDefinition class.
The following XAML code snippet demonstrates how this is done:
<telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox x:Name="gridDataBoundListBox">
<telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox.VirtualizationStrategyDefinition>
<telerikDataControls:DynamicGridVirtualizationStrategyDefinition Orientation="Horizontal" StackCount="3"/>
</telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox.VirtualizationStrategyDefinition>
</telerikDataControls:RadDataBoundListBox>
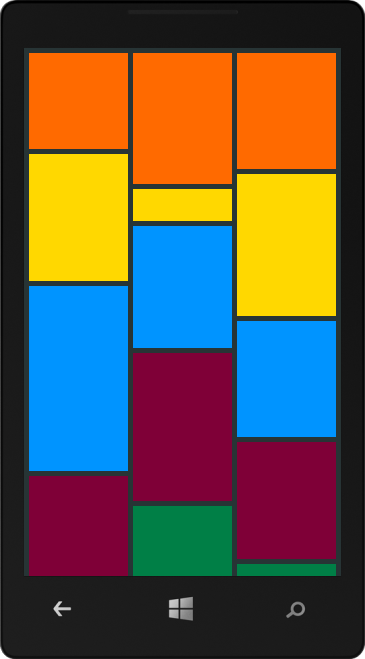
A DynamicGridVirtualizationStrategy manages the viewport by ordering the visual items in a mansory-like wrap layout. This wrap layout mode resembles the way bricks are ordered when building a house. Just as the stack layout, a wrap layout supports two orientations: hirozontal and vertical. In horizontal mode, the wrap layout strategy orders the items starting from left to right and scrolls them vertically, whereas in vertical mode - items are ordered in from top to bottom and scrolled horizontally.
Defining Orientation
You can define the wrapping orientation by setting the Orientation property of the DynamicGridVirtualizationStrategyDefinition instance.
Defining the Stack Count
Depending on the wrapping orientation, items will be ordered in columns or rows. You can choose how many columns or rows will be created by setting the StackCount property exposed by the DynamicGridVirtualizationStrategyDefinition class. For example, if the Orientation is set to be Horizontal and the StackCount is set to 3, you will get a result similar to the following: