Exporting Special Characters
This article demonstrates how you can use custom fonts to export non-ASCII characters to PDF. It contains the following sections:
Description of the problem
If you do not specify a font explicitly, any non-ASCII characters the exported DOM element contains will not be exported to the PDF file. This includes some accent characters, for example:
Example: Consider the following <div> element, which contains Swedish and Japanese characters (Kanji):
<div id="foo">Västergötland(West Gothia) 日本(Japan)</div>
#foo {
background-color: grey;
color: white;
}
This is how it looks like in the browser:
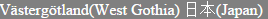
Exporting this <div> to PDF would result in the following:
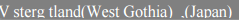
The special characters are missing in the exported file, because the standard fonts used in exporting to PDF do not support non-ASCII characters.
Solution
In order to export special characters such as some accent and diacritical marks, you have to use a custom font that supports them:
- The custom font file has to be included in the project
- The font has to be added to the RadClientExportManager's PdfSettings.Fonts collection
- The font must be set to the element you want to export (in this example the
<div>"foo").
Example
Here is a process of how to define a font that contains the desired symbols for export. It assumes you have the "Arial Unicode MS" font. You can replace it with other suitable fonts such as "DejaVu Sans".
Include the
Arial Unicode MSfont in your project'sFontsfolder. It is an extended version of the Arial font and supports Unicode characters.-
Add the font to the PdfSettings.Fonts collection.
C#
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { RadClientExportManager1.PdfSettings.Fonts.Add("Arial Unicode MS", "Fonts/ArialUnicodeMS.ttf"); }VB
Protected Sub Page_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) RadClientExportManager1.PdfSettings.Fonts.Add("Arial Unicode MS", "Fonts/ArialUnicodeMS.ttf") End Sub
-
Apply the font to the
<div>"foo":CSS
#foo { font-family: 'Arial Unicode MS'; background-color: grey; color: white; } -
Export the
<div>:ASP.NET
<telerik:RadClientExportManager runat="server" ID="RadClientExportManager1"> <pdfsettings filename="Myfile.pdf" /> </telerik:RadClientExportManager> <input type="button" onclick="exportElement()" value="export" /> <script type="text/javascript"> function exportElement() { var exp = $find("<%= RadClientExportManager1.ClientID %>"); exp.exportPDF($telerik.$("#foo")); } </script> -
Result: The special characters are correctly exported and visible in the PDF file:
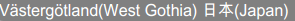
Some of the popular fonts (Segoe UI, Arial Unicode MS, Noto Serif) by default do not support the bold font. In the browser you see it working since there are many fonts the browser can fall back to, however, the exported content is not able to fall back to any font. To be able to export the bold text, you will need to add the bold font to the collection. Bold font for Segoe and bold font for Arial Unicode, etc.
Tips on defining fonts
Defining a @font-face element in the CSS of the page is equivalent to populating the Fonts collection. For example:
@font-face {
font-family: 'Arial Unicode MS';
src: url('Fonts/Arial Unicode MS.ttf');
}
You can define the special font for the global PDF export through specific CSS classes that are added to it. This means you can have it rendered on the page according to the page/browser styleshets and only change the font for export without any additional code in your markup.
.k-pdf-export, .k-pdf-export * {
font-family: 'Arial Unicode MS';
}
See Also
ClientExportManager - Export Special Characters online demo
ClientExportManager - Change the Exported Content before Export how-to article